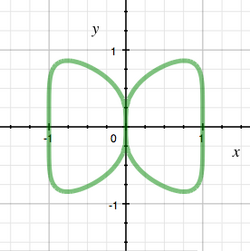
Butterfly curve (algebraic)
From HandWiki
In mathematics, the algebraic butterfly curve is a plane algebraic curve of degree six, given by the equation
- [math]\displaystyle{ x^6 + y^6 = x^2. }[/math]
The butterfly curve has a single singularity with delta invariant three, which means it is a curve of genus seven. The only plane curves of genus seven are singular, since seven is not a triangular number, and the minimum degree for such a curve is six.
The butterfly curve has branching number and multiplicity two, and hence the singularity link has two components, pictured at right.
The area of the algebraic butterfly curve is given by (with gamma function [math]\displaystyle{ \Gamma }[/math])
- [math]\displaystyle{ 4 \cdot \int_0^1 (x^2 - x^6)^{\frac{1}{6}} dx = \frac{ \Gamma(\frac{1}{6}) \cdot \Gamma(\frac{1}{3})}{3 \sqrt{\pi}} \approx 2.804, }[/math]
and its arc length s by
- [math]\displaystyle{ s \approx 9.017. }[/math]
See also
References
External links
- OEIS sequence A118292 (Decimal expansion of (Gamma(1/6)*Gamma(1/3))/(3*sqrt(Pi))) -- Sequence for the area of algebraic butterfly
- OEIS sequence A118811 (Decimal expansion of arc length of the (first) butterfly curve) -- Sequence for the arc length of algebraic butterfly curve