Biology:Pseudomonas virus gh1
| Pseudomonas virus gh1 | |
|---|---|
| |
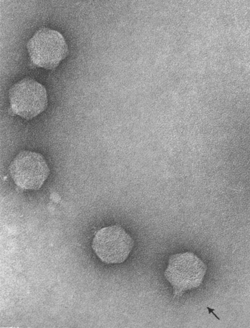
| Electron micrograph of bacteriophage gh-1 negatively stained with uranyl acetate. Magnification X 300,000. Two fibers attached to the wedge-shaped tail are visible on the bacteriophage, as indicated by an arrow. | |
| Virus classification | |
| (unranked): | Virus |
| Realm: | Duplodnaviria |
| Kingdom: | Heunggongvirae |
| Phylum: | Uroviricota |
| Class: | Caudoviricetes |
| Order: | Caudovirales |
| Family: | Autographiviridae |
| Genus: | Teseptimavirus |
| Species: | Pseudomonas virus gh1
|
Pseudomonas virus gh1 (Bacteriophage gh-1) is a bacteriophage capable of infecting susceptible strains of Pseudomonas putida.[1] It is a member of family Podoviridae, subfamily Autographivirinae.[2] It was first isolated in 1966 from a sample taken from the aeration tank at a sewage plant in East Lansing, Michigan.[citation needed]
Sedimentation analysis indicates that gh-1 carries its genetic payload in the form of a 37,359 bp linear strand of dsDNA,[3][4] inside an icosahedronal capsid 50 nm in diameter.[1]
One-step growth experiments indicate that the latent period is approximately 21 min, with a burst size of 103.[1]
It has been shown that this phage group requires an intact O-antigen on its host's outer membrane in order to successfully replicate and it is thus likely that lipopolysaccharide acts as the phage receptor.[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Lee, L.; Boezi, J. (1966). "Characterization of bacteriophage gh-1 for Pseudomonas putida." (in English). Journal of Bacteriology (American Society for Microbiology) 92 (6): 1821–1827. doi:10.1128/JB.92.6.1821-1827.1966. PMID 5958111.
- ↑ "Virus Taxonomy: 2018 Release". International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses. https://ictv.global/taxonomy. Retrieved 2018-12-07.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Kovalyova, I.; Kropinski, A. (2003). "The complete genomic sequence of lytic bacteriophage gh-1 infecting Pseudomonas putida - Evidence for close relationship to the T7 group" (in English). Journal of Virology 311 (2): 305–315. doi:10.1016/S0042-6822(03)00124-7. PMID 12842620.
- ↑ Lee, L.; Boezi, J. (1967). "Sedimentation Analysis of Pseudomonas putida A.3.12 Bacteriophage gh-1 Deoxyribonucleic Acid" (in English). Journal of Virology (American Society for Microbiology) 1 (6): 1274–1276. doi:10.1128/JVI.1.6.1274-1276.1967. PMID 5621492.
External links
- "Pseudomonas putida bacteriophage gh-1 ATCC ® 12633-B1™". https://www.lgcstandards-atcc.org/products/all/12633-B1.aspx#generalinformation. - ATCC database entry for gh-1
- "Pseudomonad phage gh-1". https://www.genome.jp/virushostdb/197783. - Virus-Host Database
Wikidata ☰ Q24808062 entry
 |

