Biology:Pharmacus
| Pharmacus | |
|---|---|
| |
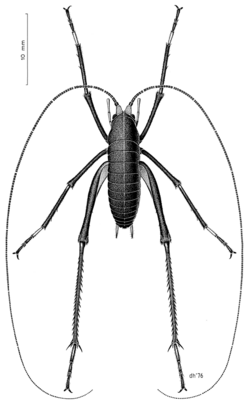
| Pharmacus montanus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Orthoptera |
| Suborder: | Ensifera |
| Family: | Rhaphidophoridae |
| Subfamily: | Macropathinae |
| Genus: | Pharmacus Pictet & Saussure, 1891 |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
Pharmacus is a genus of cave wētā in the family Rhaphidophoridae, endemic to New Zealand. All species are alpine adapted and found at high elevations in the South Island.[1] They live among rocks on high mountain ridges, often well above glaciers and vegetation.[2] Pharmacus has a geographical range that extends from Nelson south to central Otago and Fiordland.[2] They are small insects with a body length of approximately 14-20mm.[3] In this genus, females are larger than males.[3] All species exhibit dark brown to black pigmentation of the body and legs.[2] They have a dense clothing of setae and a serrated ovipositor.[3][2] When active they are lively jumpers.[3] For example, Pharmacus montanus is known as the Mount Cook flea because of its habit of leaping out of rock crevices on to mountain climbers.[4]
Taxonomy
The genus Pharmacus was first described by Pictet and de Saussure in 1893 as a monotypic taxon.[1] Pharmacus montanus was thought to be the only species in this genus.[1] However, three species were added to the genus by Richards in 1972.[1] These were Pharmacus brewsterensis (now moved to another genus), P. chapmanae and P. dumbletoni (both synonyms).[1] Six new species and three new subspecies have been recently added in 2022 by Hegg, Morgan-Richards and Trewick.[1] The six new species are Pharmacus concinnus, P. cristatus, P. notabilis, P. perfidus, P. senex, P. vallestris.[1] Three new subspecies of Pharmacus cochleatus have been described and are known as P. cochleatus rawhiti, P. cochleatus fiordensis, P. cochleatus nauclerus.[1]
Morphology
Pharmacus montanus: body length = 14mm, ovipositor = 9.9mm, foreleg = 18.7mm, mid leg = 18.7mm, hind leg = 28.6mm.[3]
Diet
Little is known about the diet of these alpine insects.[5] Pharmacus are mainly herbivorous[6] and have been observed feeding on rock lichen.[1] However, they probably prey on small invertebrates.[1] Pharmacus may also feed on the rich red algal growth that coats snow-fields during the summer season.[1]
Distribution
Pharmacus are alpine specialists and are found throughout the mountain ranges of New Zealand's South Island.[1] They are only found above the tree line and into the nival zone.[1] They have been sighted at 1300m above sea level or higher.[1] On Mt Cook P. montanus has been recorded at 3400 m asl.[6] Different species of Pharmacus have varied distributions throughout the South Island.[1] Pharmacus montanus and Pharmacus cochleatus are the two most widespread species, occupying the length of the Southern Alps from Fiordland to Kahurangi National Park.[1]
Species
- Pharmacus cochleatus (Karny, 1935)
- Pharmacus concinnus Hegg, Morgan-Richards &Trewick 2022
- Pharmacus cristatus Hegg, Morgan-Richards &Trewick 2022
- Pharmacus montanus Pictet & Saussure, 1891
- Pharmacus notabilis Hegg, Morgan-Richards &Trewick 2022
- Pharmacus perfidus Hegg, Morgan-Richards &Trewick 2022
- Pharmacus senex Hegg, Morgan-Richards &Trewick 2022
- Pharmacus vallestris Hegg, Morgan-Richards &Trewick 2022
References
- ↑ 1.00 1.01 1.02 1.03 1.04 1.05 1.06 1.07 1.08 1.09 1.10 1.11 1.12 1.13 1.14 1.15 Hegg, Danilo; Morgan-Richards, Mary; Trewick, Steven A. (2022). "High alpine sorcerers: revision of the cave wētā genus Pharmacus Pictet & de Saussure (Orthoptera: Rhaphidophoridae: Macropathinae), with the description of six new species and three new subspecies" (in en). European Journal of Taxonomy 808: 1–58–1–58. doi:10.5852/ejt.2022.808.1721. ISSN 2118-9773. https://europeanjournaloftaxonomy.eu/index.php/ejt/article/view/1721.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 Richards, Aola M. (1972). "Revision of the Rhaphidophoridae (Orthoptera) of New Zealand. Part XIV. Three alpine genera from the South Island". Journal of the Royal Society of New Zealand 2 (2): 151–174. doi:10.1080/03036758.1972.10429371. ISSN 0303-6758. https://doi.org/10.1080/03036758.1972.10429371.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "Pharmacus". http://wetageta.massey.ac.nz/Text%20files/PHARMACUS2014.html.
- ↑ Dumbleton, L. J. (1935). "The alpine weta". New Zealand Alpine Journal 6 (22): 172.
- ↑ Chinn, W. G. H.; Chinn, T. J. H. (2020). "Tracking the snow line: Responses to climate change by New Zealand alpine invertebrates". Arctic, Antarctic, and Alpine Research 52 (1): 361–389. doi:10.1080/15230430.2020.1773033. ISSN 1523-0430. https://doi.org/10.1080/15230430.2020.1773033.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Sweney, W. J. (1980). Insects of Mount Cook National Park (Thesis thesis). Lincoln College, University of Canterbury. hdl:10182/4038.
Wikidata ☰ Q7180801 entry
 |

