Biology:Grey-headed bulbul
| Grey-headed bulbul | |
|---|---|

| |
| At Udupi, Karnataka, India | |
| File:Pycnonotus priocephalus - Grey-headed Bulbul XC125720.ogg | |
| Calling in background, with louder barbet calls | |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Pycnonotidae |
| Genus: | Brachypodius |
| Species: | B. priocephalus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Brachypodius priocephalus (Jerdon, 1839)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
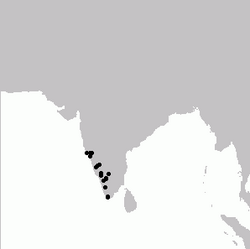
The grey-headed bulbul (Brachypodius priocephalus) is a member of the bulbul family, Pycnonotidae.[1][3] It is endemic to the Western Ghats in south-western India, and found from Goa south to Tamil Nadu at altitudes up to 1200m. It is found in dense reeds or thickets mainly near rivers and swampy areas inside forests. They have a distinctive call that reveals their presence inside dense vegetation where they are hard to spot.
Taxonomy and systematics
The grey-headed bulbul was originally described by Thomas Jerdon under the name of Brachypus priocephalus. It was moved to Brachypodius poiocephalus by Edward Blyth, who erroneously "emended" the species epithet, with subsequent confusion in the literature.[4][5][6][7] Formerly, some authorities placed this species within the genus Ixos and later Pycnonotus.[5][2]
The genus Pycnonotus was found to be polyphyletic in recent molecular phylogeny studies and the species returned to Brachypodius.[3][8][9]
The common name 'grey-headed bulbul' is also used as an alternate name for the yellow-bellied bulbul.
Description
This bulbul is resident in moist broad-leaved evergreen forest with bamboo and dense undergrowth. Its plumage is olive-green, with a medium-grey on the crown head, nape and throat. The forehead is yellow-green. The back and wings are olive-green becoming lighter towards the vent. The rump has yellowing green feathers edged in black giving a barred appearance. The flanks are dark and grey edged. The undertail coverts are grey. The beak is greenish and grey while the legs are pinkish yellow. The iris is distinctly bluish white. The tail is grey on the central feathers (the shaft being black), the outer ones are black and are broadly tipped with grey. Both sexes are similar but juveniles have the head dark olive with the yellow on the forehead duller. (Length 143-152mm; head 33-35mm; tail 74-77mm)[10][4][11] The call is a sharp chraink.[10] The call is distinct in having a single syllable unlike those of the core genus Pycnonotus members.[10]
Behaviour and ecology
Found singly or in small groups, grey-headed bulbuls actively join mixed-species foraging flocks during the non-breeding season.
Breeding
Grey-headed bulbuls breed from January to June with a peak in April. The nest is a typical platform placed inside a low bush. They build their nest over a period of a week using vines, grasses or leaves. Many nests in a study in the Silent Valley National park were found to be made on saplings of Syzygium species or in reeds of Ochlandra travancorica. The typical clutch is one egg or sometimes two eggs that are incubated for 12 to 14 days. Eggs are sometimes destroyed and eaten by palm squirrels (Funambulus tristriatus).[12] The eggs are pale pink to lavender and flecked in red, more densely on the broad end.[13] Both parents take part in incubation and feeding.[14] The nestlings leave the nest after 11 to 13 days.
Feeding
The diet consists mainly of fruits (>65%) and invertebrates (>30%). Fruits include those of Symplocos cochinchinensis, Antidesma menasu, Clerodendrum viscosum, Syzygium cumini, Litsea floribunda, Maesa indica, Callicarpa tomentosa, Leea indica and Lantana camara.[15][16]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 BirdLife International (2016). "Brachypodius priocephalus". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2016: e.T22712619A94339381. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22712619A94339381.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22712619/94339381. Retrieved 19 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Eydoux, Fortune; Souleyet, L.F.A. (1841). Voyage Autour du Monde sur la Corvette La Bonite. Paris: Arthus Bertrand. pp. 86–88. https://archive.org/stream/zoologie1111eydou#page/85/mode/1up.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds. "Family Pycnonotidae". International Ornithological Congress. https://www.worldbirdnames.org/Family/Pycnonotidae.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Jerdon TC (1863). The birds of India. Volume 2 part 1. Military Orphan Press, Calcutta. p. 89. https://archive.org/stream/birdsofindiabein21jerd#page/89/mode/1up.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Dickinson, E.C.; R.W.R.J. Dekker; S. Eck; S. Somadikarta (2002). "Systematic notes on Asian birds. 26. Types of the Pycnonotidae". Zool. Verh. Leiden 340: 115–160. http://www.repository.naturalis.nl/document/46724.
- ↑ Baker, ECS (1930). Fauna of British India. Birds. 7 (2nd ed.). Taylor and Francis, London. p. 88. https://archive.org/stream/BakerFbiBirds7/BakerFBI7#page/n95/mode/1up/.
- ↑ Baker, ECS (1922). Fauna of British India. Birds Volume 1. Taylor and Francis, London. pp. 425–426. https://archive.org/stream/birds01bakeiala#page/425/mode/1up/.
- ↑ Moyle RG; BD Marks (2006). "Phylogenetic relationships of the bulbuls (Aves: Pycnonotidae) based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequence data". Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 40 (3): 687–695. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2006.04.015. PMID 16750401. Archived from the original on 2010-06-16. https://web.archive.org/web/20100616200146/http://wfsc.tamu.edu/bdmarks/Publications_files/Moyle-2006-Phylogenetic%20relatio.pdf.
- ↑ Shakya, Subir B.; Sheldon, Frederick H. (2017). "The phylogeny of the world's bulbuls (Pycnonotidae) inferred using a supermatrix approach". Ibis 159 (3): 498–509. doi:10.1111/ibi.12464. ISSN 0019-1019.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 Rasmussen, P.C.; J.C. Anderton (2005). Birds of South Asia: the Ripley guide. 2. Smithsonian Institution & Lynx Edicions. pp. 335–336. ISBN 84-87334-67-9.
- ↑ Oates, EW (1889). Fauna of British India. Birds Volume 1. Taylor and Francis, London. p. 296. https://archive.org/stream/birdsindia01oaterich#page/296/mode/1up.
- ↑ Vijayan, V.S., and Balakrishnan, Peroth. (2005). Status, Distribution and Ecology of the Grey-headed Bulbul Pycnonotus priocephalus in Western Ghats, India. Final Report submitted to Ministry of Environment and Forests, Govt. of India. Sálim Ali Centre for Ornithology Natural History, Coimbatore.
- ↑ Ali S; SD Ripley (1996). Handbook of the birds of India and Pakistan. 6 (2nd ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 70–71.
- ↑ Balakrishnan Peroth (2010). "Parental care strategies of grey-headed bulbul, Pycnonotus priocephalus in the Western Ghats, South India". Current Science 98 (5): 673–680. http://www.ias.ac.in/currsci/10mar2010/673.pdf.
- ↑ Balakrishnan, Peroth. (2011). "Breeding biology of the Grey-headed Bulbul Pycnonotus priocephalus (Aves: Pycnonotidae) in the Western Ghats, India". Journal of Threatened Taxa 3 (1): 1415–1424. doi:10.11609/jott.o2381.1415-24.
- ↑ Balakrishnan, Peroth (2014). "Foraging behaviour of the Near Threatened Grey-headed Bulbul Pycnonotus priocephalus in relation to seasons and breeding stages". Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 111 (1): 10–18. doi:10.17087/bnhs/2014/v111i1/56520.
Other sources
- Balakrishnan, Peroth (2007). Status, distribution and ecology of Grey-headed Bulbul Pycnonotus priocephalus in the Western Ghats, India. Ph.D. thesis. Bharathiar University, Coimbatore.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q943401 entry
 |