Biology:Black-bellied wren
| Black-bellied wren | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Troglodytidae |
| Genus: | Pheugopedius |
| Species: | P. fasciatoventris
|
| Binomial name | |
| Pheugopedius fasciatoventris (Lafresnaye, 1845)
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
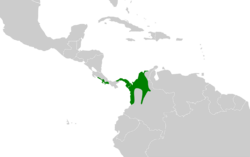
The black-bellied wren (Pheugopedius fasciatoventris) is a species of bird in the family Troglodytidae. It is found in Colombia, Costa Rica, and Panama.[1]
Taxonomy and systematics
The black-bellied wren has three subspecies, the nominate Pheugopedius fasciatoventris fasciatoventris, P. f. melanogaster, and P. f. albigularis.[1]
Description
Male black-bellied wrens weigh 23.5 to 34.5 g (0.83 to 1.22 oz) and females 19.5 to 28.5 g (0.69 to 1.01 oz). Adults of all three subspecies have a rich chestnut back and tail; the latter has black bars. They have a white supercilium of varying size above a grayish face and are white on the chin, throat, and breast. All three have a black belly, but that of P. f. melanogaster is unmarked while those of the other two subspecies have thin white bars.[2]
Distribution and habitat
P. f. melanogaster is the northernmost subspecies; it is found from the Gulf of Nicoya in western Costa Rica through western Panama to the Canal Zone. P. f. albigularis is found from the Canal Zone into Colombia's Chocó Department. The nominate P. f. fasciatoventris is found in northwestern and central Colombia east to the foothills of the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta and south into the Cauca and Magdalena valleys. The species inhabits the interior and edges of primary and secondary forest and is often associated with streams.[2][3]
Behavior
Feeding
The black-bellied wren forages mainly in the canopy and sub-canopy of both the forest interior and its edges. It also sometimes forages in the understory and on the ground, but always in dense cover. It preys on small arthropods but details are scant.[2]
Breeding
The black-bellied wren nests mostly in forest edges, usually near the ground in vine tangles. The nests are domed with a side entrance and constructed by both sexes of strips of palm and sugar cane leaves and lined with softer plant material. The clutch size is two. It appears that only the female incubates the eggs. The species' nests are heavily predated.[2]
Vocalization
Both sexes of the black-bellied wren have large song repertoires; one male was recorded with 38 different songs and a female with 19.[2] Multiple examples are available at Xeno-canto [1] and Cornell's Macaulay Library [2].
Status
The IUCN has assessed the black-bellied wren as being of Least Concern. However, its population "is suspected to be in decline owing to ongoing habitat destruction and fragmentation."[3]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P. (January 2021). "IOC World Bird List (v 11.1)". https://www.worldbirdnames.org/.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 Logue, D. M. (2020). Black-bellied Wren (Pheugopedius fasciatoventris), version 1.0. In Birds of the World (T. S. Schulenberg, Editor). Cornell Lab of Ornithology, Ithaca, NY, USA. https://doi.org/10.2173/bow.blbwre1.01 retrieved 3 June 2021
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedIUCN
Wikidata ☰ Q4741856 entry
 |



