Chemistry:Fialuridine
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
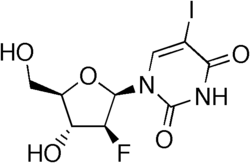
| Other names | 2′-Fluoro-5-iodouracil |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C9H10FIN2O5 |
| Molar mass | 372.091 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Fialuridine, or 1-(2-deoxy-2-fluoro-1-D-arabinofuranosyl)-5-iodouracil (FIAU), is a nucleoside analogue that was investigated as a potential therapy for hepatitis B virus infection. In a 1993 clinical study at the NIH, unexpected toxicity led to the death of 5 out of 15 patients from liver failure alongside lactic acidosis; two further participants required liver transplantation. It is suspected that the toxicity of fialuridine was a result of mitochondrial damage caused by the incorporation of fialuridine into mitochondrial DNA via its 3'-hydroxyl moiety, leading to impaired DNA synthesis. This toxicity was unusual in that it was not predicted by animal studies.[1][2][3]
References
- ↑ "Mechanisms of drug-induced liver injury: from bedside to bench". Nature Reviews. Gastroenterology & Hepatology 8 (4): 202–11. April 2011. doi:10.1038/nrgastro.2011.22. PMID 21386809.
- ↑ "Hepatic failure and lactic acidosis due to fialuridine (FIAU), an investigational nucleoside analogue for chronic hepatitis B". The New England Journal of Medicine 333 (17): 1099–105. October 1995. doi:10.1056/NEJM199510263331702. PMID 7565947.
- ↑ Thomson, Larry (1 March 1994). "The Cure that Killed". Discover Magazine. http://discovermagazine.com/1994/mar/thecurethatkille345#.UnVB6ErVlkd. Retrieved 2 November 2013.
 |

