Chemistry:Methylammonium chloride
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Methylazanium chloride
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Methanaminium chloride | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| CH3NH3Cl | |
| Molar mass | 67.51804 g/mol |
| Appearance | White crystals [1] |
| Hazards[2] | |
| Main hazards | irritant |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H302, H315, H319, H335 | |
| P261, P305+351+338 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
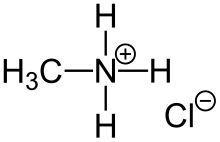
Methylammonium chloride in an organic halide with a formula of CH3NH3Cl. It is an ammonium salt composed of methylamine and hydrogen chloride. One potential application for the methylammonium halides is in the production of perovskite solar cells.[3][4] The methyl group and other hydrogen atoms are bonded covalently to the nitrogen, with the chloride bonded ionically.
References
- ↑ "Methylammonium chloride". https://www.greatcellsolarmaterials.com/methylammonium-chloride.html.
- ↑ "GESTIS-Stoffdatenbank". https://gestis.dguv.de/data?name=021960.
- ↑ Li, Hangqian. (2016). "A modified sequential deposition method for fabrication of perovskite solar cells". Solar Energy 126: 243–251. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2015.12.045. Bibcode: 2016SoEn..126..243L.
- ↑ Zhao, X. (2021). "Methylammonium Chloride reduces the bandgap width and trap densities for efficient perovskite photodetectors". Journal of Materials Science 56: 9242–9253. doi:10.1007/s10853-021-05840-2.
 |

