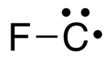Chemistry:Fluoromethylidyne
|
| |||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |||
| Infobox references | |||
}} |Section1=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Identifiers
|-
|
|
|-
|
|
|-
|
|-
|
|
|-
| colspan="2" |
- InChI=1S/CF/c1-2
 Key: ISOSXCFSIDVNNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Key: ISOSXCFSIDVNNC-UHFFFAOYSA-N
|-
| colspan="2" |
- [C]F
|- |Section2=! colspan=2 style="background: #f8eaba; text-align: center;" |Properties
|-
|
| CF•
|- | Molar mass
| 31.0091 g mol−1
|- }} Fluoromethylidyne is not a stable chemical species but a metastable radical containing one highly reactive carbon atom bound to one fluorine atom with the formula CF.[1] The carbon atom has a lone-pair and a single unpaired (radical) electron in the ground state.[2]
Ground-state fluoromethylidyne radicals can be produced by the ultraviolet photodissociation of dibromodifluoromethane at 248 nanometer wavelength.[3]
It readily and irreversibly dimerises to difluoroacetylene, also known as difluoroethyne, perfluoroacetylene, or di- or perfluoroethylyne. Under certain conditions it can hexamerise to hexafluorobenzene.
See also
References
- ↑ F. J. Grieman; A. T. Droege; P. C. Engelking (March 1983). "The a4Σ−–X2Π transition in CF: A measurement of the term energy and bond length of a fluoromethylidyne metastable". Journal of Chemical Physics 78 (5): 2248–2254. doi:10.1063/1.445070.
- ↑ Ruzsicska, B. P.; Jodhan, A.; Choi, H. K. J.; Strausz, O. P.; Bell, T. N. (1983). "Chemistry of carbynes: reaction of CF, CCl, and CBr with alkenes". J. Am. Chem. Soc. 105 (8): 2489–2490. doi:10.1021/ja00346a072.
- ↑ J. Peeters; J. Van Hoeymissen; S. Vanhaelemeersch; D. Vermeylen (February 1992). "Absolute rate constant measurements of CF(X2Π) reactions. 1. Reactions with O2, F2, Cl2 and NO". Journal of Physical Chemistry 96 (3): 1257–1263. doi:10.1021/j100182a043.
 |