Chemistry:Corosolic acid
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2α,3β-Dihydroxyurs-12-en-28-oic acid
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(1S,2R,4aS,6aS,6bR,8aR,10R,11R,12aR,12bR,14bS)-10,11-Dihydroxy-1,2,6a,6b,9,9,12a-heptamethyl-1,3,4,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,12b,13,14b-octadecahydropicene-4a(2H)-carboxylic acid | |
| Other names
Glucosol; Corsolic acid; Colosic acid; 2α-Hydroxyursolic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C30H48O4 | |
| Molar mass | 472.710 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
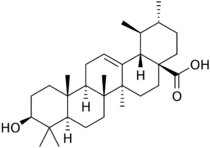
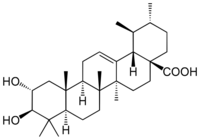
Corosolic acid is a pentacyclic triterpene acid found in Lagerstroemia speciosa. It is similar in structure to ursolic acid, differing only in the fact that it has a 2-alpha-hydroxy attachment.[1]
References
- ↑ Baba, Kosuke; Hiramatsu, Reiko; Suradej, Benjamart; Tanigaki, Riho; Koeda, Sayaka; Waku, Tomonori; Kataoka, Takao (2018). "Asiatic Acid, Corosolic Acid, and Maslinic Acid Interfere with Intracellular Trafficking and N-Linked Glycosylation of Intercellular Adhesion Molecule-1.". Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 41 (12): 1757–1768. doi:10.1248/bpb.b18-00276. PMID 30504678.
 |