Biology:Spanish painted frog
| Spanish painted frog | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification Error creating thumbnail: Unable to save thumbnail to destination
| |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Alytidae |
| Genus: | Discoglossus |
| Species: | D. jeanneae
|
| Binomial name | |
| Discoglossus jeanneae Busack, 1986
| |
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Discoglossus galganoi jeanneae Busack, 1986 | |
The Spanish painted frog (Discoglossus jeanneae), in Spanish sapillo pintojo meridional, is a species of frog in the family Alytidae (formerly Discoglossidae). It is endemic to Spain .[1][2]
Description
The Spanish painted frog is a medium-sized amphibian. The top of the frog is predominantly colored with dark browns in the form of spots or stripes, and its underbelly is usually white or yellow. The males have webbing between their hind toes, but the webbing is not found in females or adolescent males. During the mating season, the males develop black calluses on the toe webbing, throat, belly, and parts of the forefeet.[3]
This species is very closely related to the Iberian painted frog, but they differ significantly. The Spanish painted frog has a shorter snout and smaller forefeet than its Iberian counterpart.
Distribution and habitat
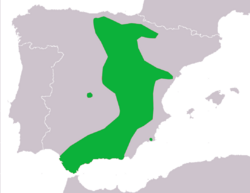
The Spanish painted frog is endemic to the southern, eastern, and north-eastern regions of Spain, but is more densely populated in the southern regions.[3] It mostly lives in open areas, pine groves and shrublands from sea level to roughly 2,000 m above sea level.[1]
Biology
Not much is known about the biology of the Spanish painted frog, but it is believed to be very similar to that of the Iberian painted frog. It is believed to be active year-round. Eggs are usually laid in small, shallow bodies of water.
Its diet consists mostly of insects and worms, though it has also been known to eat the young of other frogs and toads.[3] Most activity is at night. The tadpoles eat plant material.
Status
The Spanish painted frog is classified as near threatened according to the IUCN Red List, and results from a series of droughts throughout most of its range. A high probability exists that isolated populations have become extinct along the Mediterranean coast.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bosch, J.; Tejedo, M.; Lizana, M.; Martínez-Solano, I.; Salvador, A.; García-París, M.; Gil, E.R.; Paniagua, C.D. et al. (2009). "Discoglossus jeanneae". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2009: e.T6713A12798514. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2009.RLTS.T6713A12798514.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/6713/12798514.
- ↑ Frost, Darrel R. (2015). "Discoglossus jeanneae Busack, 1986". Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History. http://research.amnh.org/vz/herpetology/amphibia/Amphibia/Anura/Alytidae/Discoglossus/Discoglossus-jeanneae. Retrieved 5 September 2015.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Spanish Painted Frog (Discoglossus jeanneae)". http://www.arkive.org/spanish-painted-frog/discoglossus-jeanneae/.
Wikidata ☰ Q302887 entry
 |