Biology:TOP3A
 Generic protein structure example |
DNA topoisomerase 3-alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the TOP3A gene.[1][2]
Function
This gene encodes a DNA topoisomerase, an enzyme that controls and alters the topologic states of DNA during transcription. This enzyme catalyzes the transient breaking and rejoining of a single strand of DNA which allows the strands to pass through one another, thus reducing the number of supercoils and altering the topology of DNA. This enzyme forms a complex with BLM which functions in the regulation of recombination in somatic cells.[2]
Meiosis
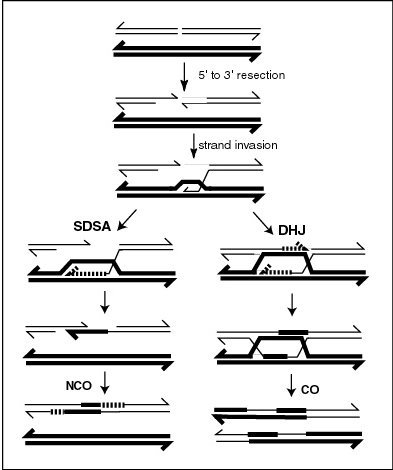
Recombination during meiosis is often initiated by a DNA double-strand break (DSB). During recombination, sections of DNA at the 5' ends of the break are cut away in a process called resection. In the strand invasion step that follows, an overhanging 3' end of the broken DNA molecule then "invades" the DNA of an homologous chromosome that is not broken forming a displacement loop (D-loop). After strand invasion, the further sequence of events may follow either of two main pathways leading to a crossover (CO) or a non-crossover (NCO) recombinant (see Genetic recombination and see Figure). The pathway leading to a NCO is referred to as Synthesis-dependent strand annealing (SDSA).
In the plant Arabidopsis thaliana, multiple mechanisms limit meiotic COs.[3] During meiosis TOP3A and RECQ4A/B helicase antagonize formation of COs in parallel to FANCM helicase.[3] Sequela-Arnaud et al.[3] suggested that CO numbers are restricted because of the long-term costs of CO recombination, that is, the breaking up of favorable genetic combinations of alleles built up by past natural selection.
In the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the topoisomerase III (TOP3)-RMI1 heterodimer (that catalyzes DNA single-strand passage) forms a conserved complex with Sgs1 helicase (an ortholog of the human Bloom syndrome helicase). This complex promotes early formation of NCO recombinants during meiosis[4] The TOP3-RMI1 strand passage activity appears to have two important functions during meiosis.[4] First, strand passage activity is employed early in coordination with Sgs1 helicase to promote proper recombination pathway choice. Second, strand passage activity is used later, independently of Sgs1 helicase, to prevent the persistence of unresolvable strand entanglements in recombination intermediates.
Interactions
TOP3A has been shown to interact with Bloom syndrome protein.[5][6][7][8]
References
- ↑ "Gene for topoisomerase III maps within the Smith-Magenis syndrome critical region: analysis of cell-cycle distribution and radiation sensitivity". American Journal of Medical Genetics 75 (1): 104–8. Jan 1998. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1096-8628(19980106)75:1<104::AID-AJMG21>3.0.CO;2-P. PMID 9450867.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Entrez Gene: TOP3A topoisomerase (DNA) III alpha". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=7156.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 "Multiple mechanisms limit meiotic crossovers: TOP3α and two BLM homologs antagonize crossovers in parallel to FANCM". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 112 (15): 4713–8. Apr 2015. doi:10.1073/pnas.1423107112. PMID 25825745. Bibcode: 2015PNAS..112.4713S.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Top3-Rmi1 DNA single-strand decatenase is integral to the formation and resolution of meiotic recombination intermediates". Molecular Cell 57 (4): 583–94. Feb 2015. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2015.01.020. PMID 25699707.
- ↑ "The Bloom's syndrome gene product interacts with topoisomerase III". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (13): 9636–44. Mar 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.13.9636. PMID 10734115.
- ↑ "Cleavage of the Bloom's syndrome gene product during apoptosis by caspase-3 results in an impaired interaction with topoisomerase IIIalpha". Nucleic Acids Research 29 (15): 3172–80. Aug 2001. doi:10.1093/nar/29.15.3172. PMID 11470874.
- ↑ "Evidence for BLM and Topoisomerase IIIalpha interaction in genomic stability". Human Molecular Genetics 10 (12): 1287–98. Jun 2001. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.12.1287. PMID 11406610.
- ↑ "Replication protein A physically interacts with the Bloom's syndrome protein and stimulates its helicase activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (31): 23500–8. Aug 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001557200. PMID 10825162.
Further reading
- "Human TOP3: a single-copy gene encoding DNA topoisomerase III". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 93 (8): 3653–7. Apr 1996. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3653. PMID 8622991. Bibcode: 1996PNAS...93.3653H.
- "Overexpression of a truncated human topoisomerase III partially corrects multiple aspects of the ataxia-telangiectasia phenotype". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 94 (9): 4538–42. Apr 1997. doi:10.1073/pnas.94.9.4538. PMID 9114025. Bibcode: 1997PNAS...94.4538F.
- "Cloning and characterization of the 5'-flanking region for the human topoisomerase III gene". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 273 (40): 26130–7. Oct 1998. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.40.26130. PMID 9748294.
- "Purification and characterization of human DNA topoisomerase IIIalpha". Nucleic Acids Research 27 (12): 2443–50. Jun 1999. doi:10.1093/nar/27.12.2443. PMID 10352172.
- "Human RecQ5beta, a large isomer of RecQ5 DNA helicase, localizes in the nucleoplasm and interacts with topoisomerases 3alpha and 3beta". Nucleic Acids Research 28 (7): 1647–55. Apr 2000. doi:10.1093/nar/28.7.1647. PMID 10710432.
- "The Bloom's syndrome gene product interacts with topoisomerase III". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (13): 9636–44. Mar 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.13.9636. PMID 10734115.
- "Differential expression of human topoisomerase IIIalpha during the cell cycle progression in HL-60 leukemia cells and human peripheral blood lymphocytes". Experimental Cell Research 256 (1): 225–36. Apr 2000. doi:10.1006/excr.1999.4778. PMID 10739669.
- "Replication protein A physically interacts with the Bloom's syndrome protein and stimulates its helicase activity". The Journal of Biological Chemistry 275 (31): 23500–8. Aug 2000. doi:10.1074/jbc.M001557200. PMID 10825162.
- "Expression of topoisomerase IIIalpha in normal and neoplastic tissues determined by immunohistochemistry using a novel monoclonal antibody". British Journal of Cancer 83 (4): 498–505. Aug 2000. doi:10.1054/bjoc.2000.1293. PMID 10945498.
- "Evidence for BLM and Topoisomerase IIIalpha interaction in genomic stability". Human Molecular Genetics 10 (12): 1287–98. Jun 2001. doi:10.1093/hmg/10.12.1287. PMID 11406610.
- "Cleavage of the Bloom's syndrome gene product during apoptosis by caspase-3 results in an impaired interaction with topoisomerase IIIalpha". Nucleic Acids Research 29 (15): 3172–80. Aug 2001. doi:10.1093/nar/29.15.3172. PMID 11470874.
- "Genes in a refined Smith-Magenis syndrome critical deletion interval on chromosome 17p11.2 and the syntenic region of the mouse". Genome Research 12 (5): 713–28. May 2002. doi:10.1101/gr.73702. PMID 11997338.
- "Dual localization of human DNA topoisomerase IIIalpha to mitochondria and nucleus". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99 (19): 12114–9. Sep 2002. doi:10.1073/pnas.192449499. PMID 12209014. Bibcode: 2002PNAS...9912114W.
- "The Bloom's syndrome helicase stimulates the activity of human topoisomerase IIIalpha". Nucleic Acids Research 30 (22): 4823–9. Nov 2002. doi:10.1093/nar/gkf611. PMID 12433984.
- "A novel ubiquitin ligase is deficient in Fanconi anemia". Nature Genetics 35 (2): 165–70. Oct 2003. doi:10.1038/ng1241. PMID 12973351.
- "Physical and functional interaction between the Bloom's syndrome gene product and the largest subunit of chromatin assembly factor 1". Molecular and Cellular Biology 24 (11): 4710–9. Jun 2004. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.11.4710-4719.2004. PMID 15143166.
- "BLAP75, an essential component of Bloom's syndrome protein complexes that maintain genome integrity". The EMBO Journal 24 (7): 1465–76. Apr 2005. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600622. PMID 15775963.

