Chemistry:Meta-Diethynylbenzene dianion
| It has been suggested that this page be merged into ortho-Diethynylbenzene dianion. (Discuss) Proposed since May 2018. |
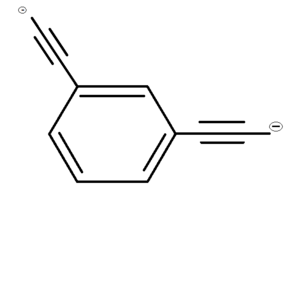 Meta-diethynylbenzene dianion
| |
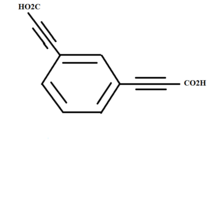 The compound C
6H 4(C 3HO 2) 2 used for the synthesis of Meta-diethynylbenzene dianion | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Meta-diethynylbenzene dianion
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4C2−4 | |
| Hazards | |
| Main hazards | Extremely corrosive |
| Related compounds | |
Related bases
|
Ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion Para-diethynylbenzene dianion |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
The meta-diethynylbenzene dianion is a structural isomer of the ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion. The meta-diethynylbenzene dianion is not as strong as ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion, but it is still the second-strongest superbase. Like the ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion, the meta-diethynylbenzene dianion exists in the gas state, contrary to the other bases and superbases which exist in the solution state. In the meta-diethynylbenzene dianion, the two negatively charged ethynyl (−C2H−2) groups are bonded to the first and third carbon atoms of the benzene ring. But in the ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion, the ethynyl groups are bonded to the first and second carbon atoms of the benzene ring. Like Ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion, Meta-diethynylbenzene dianion has no known use.
Synthesis
- Step 1
- A sample of meta-C6H4(C3HO2)2 is taken.
- Step 2
- In this next step, the parent compound is subjected through electrospray ionization (ESI) and consequently, loses two Hydrogen atoms and therefore, acquires a charge of −2. The new compound's chemical formula is [C6H4(C3O2)2]2−
- Step 3
- The ionized parent compound [C6H4(C3O2)2]2− is subjected to collision-induced dissociation (CID), because of which, one of the carboxylate anion loses a Carbon dioxide molecule to become [C6H4(C5O2)]2−.
- Step 4
- The meta-[C6H4(C3O2)2]2− compound is again subjected to collision-induced dissociation, because of which, the other carboxylate anion loses the other Carbon dioxide molecule and becomes meta-[C6H4(C5O2)]2−
- Step 5
- Therefore, the meta-diethynylbenzene dianion [C6H4(C2)2]2− is formed, having lost, in total, two hydrogen atoms and two molecules of carbon dioxide.
The same process can generate either ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion and Meta-diethynylbenzene dianion depending on which isomer of the original compound is used.
Summary
- [math]\ce{ \overset{}{C6H4(C3HO2)2 ->[\ce{ESI}][] [C6H4(C3O2)2]^{2-} ->[\ce{CID}][] [C6H4(C5O2)]^{2-} ->[\ce{CID}][] [C6H4(C2)2]^{2-}} }[/math]
- Metadiethynylbenzene dianion.png
The compound after the first stage of collision-induced dissociation having lost a carbon dioxide molecule and retaining the negative charge.
- Meta-diethynylbenzene.png
meta-[C
6H
4(C
5O
2)]2− is subjected to collision-induced dissociation for the second time losing another Carbon dioxide molecule but retaining the negative charge. Thus, the compound, Meta-diethynylbenzene dianion is formed.
See also
List of the other isomers
- Ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion
- Para-diethynylbenzene dianion
References
Poad, Berwyck L. J.; Reed, Nicholas D.; Hansen, Christopher S.; Trevitt, Adam J.; Blanksby, Stephen J.; Mackay, Emily G.; Sherburn, Michael S.; Chan, Bun et al. (12 January 2018). "Preparation of an ion with the highest calculated proton affinity: ortho -diethynylbenzene dianion". Chemical Science 7 (9). doi:10.1039/C6SC01726F. http://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlehtml/2016/sc/c6sc01726f. Retrieved 12 January 2018.

