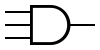
Engineering:Fan-in
Fan-in is the number of inputs a logic gate can handle.[1] For instance the fan-in for the AND gate shown in the figure is 3.[2] Physical logic gates with a large fan-in tend to be slower than those with a small fan-in. This is because the complexity of the input circuitry increases the input capacitance of the device.[3][4] Using logic gates with higher fan-in will help in reducing the depth of a logic circuit; this is because circuit design is realized by the target logic family at a digital level, meaning any large fan-in logic gates are simply the smaller fan-in gates chained together in series at a given depth to widen the circuit instead.
Fan-in tree of a node refers to a collection of signals that contribute to the input signal of that node.[5]
In quantum logic gates the fan-in always has to be equal to the number of outputs, the fan-out. Gates for which the numbers of inputs and outputs differ would not be reversible (unitary) and are therefore not allowed.
See also
- Fan-out, a related concept, which is the number of inputs that a given logic output drives.
References
- ↑ "fan-in and fan-out". https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/programmable/quartushelp/13.0/mergedProjects/reference/glossary/def_fan.htm. "Fan-in refers to the maximum number of input signals that feed the input equations of a logic cell."
- ↑ JoCavanagh (21 December 2017). Digital Design and Verilog HDL Fundamentals. CRC Press. pp. 3–. ISBN 978-1-351-83456-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=yAlEDwAAQBAJ&pg=SA3-PA28.
- ↑ Dimitrios Soudris; Peter Pirsch; Erich Barke (29 June 2003). Integrated Circuit Design: Power and Timing Modeling, Optimization and Simulation: 10th International Workshop, PATMOS 2000, Göttingen, Germany, September 13-15, 2000 Proceedings. Springer. pp. 274–. ISBN 978-3-540-45373-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=uh-qCAAAQBAJ&pg=PA274.
- ↑ Singh Ajay Kumar (30 June 2010). Digital Vlsi Design. PHI Learning Pvt. Ltd.. pp. 138–. ISBN 978-81-203-4187-6. https://books.google.com/books?id=Gr023E8Kd5QC&pg=PA138.
- ↑ "Fan-in tree analysis: a new fault isolation tool". IEEE. doi:10.1109/smelec.1996.616446. "Fan-in tree is a collection of subsequent fan-in signals with respect to a given node."
de:Fan-Out#Fan-In
 |