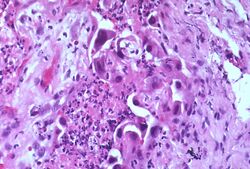
Medicine:Atypia
Atypia (from Greek, a + typos, without type; a condition of being irregular or nonstandard)[1] is a histopathologic term for a structural abnormality in a cell, i.e. it is used to describe atypical cells.
Atypia can be caused by an infection or irritation. if , for example it were diagnosed in a Pap smear, In the uterus it is more likely to be precancerous.
The related concept of dysplasia refers to an abnormality of development,[2] and includes abnormalities on larger, histopathologic scales.
Example features
Features that constitute atypia have different definitions for different diseases, but often include the following nucleus abnormalities:[3]
- Enlargement
- Pleomorphism
- Nuclear polychromasia, which means variability in nuclear chromatin content.[4] Polychromasia otherwise refers to a disease of immature red blood cells.
- Numerous mitotic figures
Examples for Barrett's esophagus
In Barrett's esophagus, features that are classified as atypia but not as dysplasia are mainly:[5]
- Nuclear stratification, wherein cell nuclei, which are normally located nearly at the same level between adjacent cells, are instead located at different levels.
- Crowding
- Hyperchromatism
- Prominent nucleoli
Prognosis
It may or may not be a precancerous indication associated with later malignancy, but the level of appropriate concern is highly dependent on the context with which it is diagnosed.
For example, already differentiated, specialised cells such as epithelia displaying "cellular atypia" are far less likely to become problematic (cancerous/malignant) than are myeloid progenitor cells of the immune system. The 'further back' in an already specialised, differentiated cell's lineage, the more problematic cellular atypia is likely to be. This is due to the conferring of such atypia to progeny-cells further down the lineage of that cell type.
See also
- Irregularity
- List of biological development disorders
References
- ↑ Mosby's Medical Dictionary (8th edition). Elsevier.
- ↑ "dysplasia" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- ↑ "General oncology". https://www.amboss.com/us/knowledge/General_oncology. Retrieved 2020-01-29.
- ↑ Page 27 in: Sumant Sharma, Yogesh Chhabra (2012). MCQs in Objective Pathology with Explanations. Jaypee Brothers Publishers. ISBN 9789350259047.
- ↑ "Definition and Characteristics of Dysplasia in Barrett's Esophagus". http://www.pathology.washington.edu/about/education/barretts/page2.php. Retrieved 2019-09-27.
 |