Medicine:McKusick–Kaufman syndrome
| McKusick–Kaufman syndrome | |
|---|---|
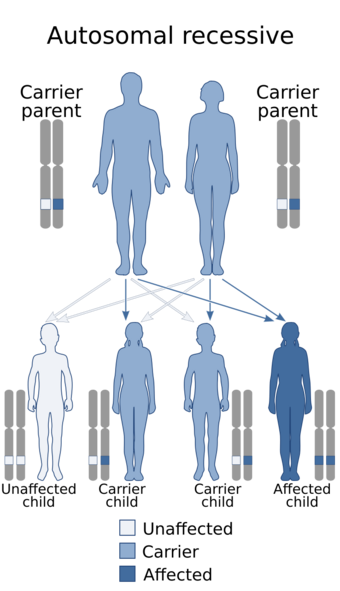 | |
| McKusick–Kaufman syndrome is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner |
McKusick–Kaufman syndrome is a genetic condition associated with MKKS.
The condition is named for Dr. Robert L. Kaufman and Victor McKusick.[1] It is sometimes known by the abbreviation MKS.[2] In infancy it can be difficult to distinguish between MKS and the related Bardet–Biedl syndrome, as the more severe symptoms of the latter condition rarely materialise before adulthood.[3]
McKusick-Kaufman syndrome affects 1 in 10,000 people in the Old Order Amish population. A case frequency outside of this population has not been established.[4]
Presentation
Clinically, McKusick–Kaufman syndrome is characterized by a combination of three features: postaxial polydactyly, heart defects, and genital abnormalities:[citation needed]
- Vaginal atresia with hydrometrocolpos
- Double vagina and/or uterus.
- Hypospadias, chordee (a downward-curving penis), and undescended testes (cryptorchidism).
- ureter stenosis or ureteric atresia
Genetics
MKS is inherited in an autosomal recessive dominance pattern.[5] Both parents of the affected must be heterozygous carriers of the pathogenic variant. Heterozygous carriers for MKS show no symptoms of the disorder, nor can they develop the disorder. Each child of these carriers has a 1/4 chance of being affected by MKS, a 1/2 chance of being carriers themselves, and a 1/4 chance of being unaffected and a non carrier.[citation needed]
Diagnosis
Clinical findings support the diagnosis of MKS, including identification of biallelic pathogenetic variants. Diagnosis additionally requires ruling out Bardet-Biedl Syndrome.[6]
Treatment
Treatments are available for accompanying symptoms of MKS, including addressing polydactyly and congenital heart defects.[7]
See also
References
- ↑ McKusick-Kaufman syndrome at Who Named It?
- ↑ Abbreviation cited at Genetics Home Reference.
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home. "McKusick-Kaufman syndrome" (in en). https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/mckusick-kaufman-syndrome#diagnosis.
- ↑ Reference, Genetics Home. "McKusick-Kaufman syndrome" (in en). https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/mckusick-kaufman-syndrome#statistics.
- ↑ Slavotinek AM, "McKusick-Kaufam Syndrome", GeneReviews, 1993-2015
- ↑ Slavotinek, Anne M. (1993), Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Pagon, Roberta A. et al., eds., "McKusick-Kaufman Syndrome", GeneReviews® (University of Washington, Seattle), PMID 20301675, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1502/, retrieved 2018-11-07
- ↑ Slavotinek, Anne M. (1993), Adam, Margaret P.; Ardinger, Holly H.; Pagon, Roberta A. et al., eds., "McKusick-Kaufman Syndrome", GeneReviews® (University of Washington, Seattle), PMID 20301675, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1502/, retrieved 2018-11-07
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

