Social:Iroquoian languages
| Iroquoian | |
|---|---|
| Geographic distribution | eastern North America |
| Linguistic classification | One of the world's primary language families |
| Proto-language | Proto-Iroquoian |
| Subdivisions |
|
| ISO 639-2 / 5 | iro |
| Glottolog | iroq1247[1] |
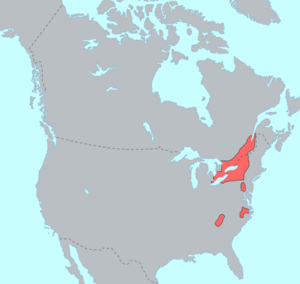 Pre-European contact distribution of the Iroquoian languages. | |
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.[2]
As of 2020, almost all surviving Iroquoian languages are severely or critically endangered, with some languages having only a few elderly speakers remaining. The two languages with the most speakers, Mohawk (Kenien'kéha) in New York and Canada, and Cherokee in Oklahoma and North Carolina, are spoken by less than 10% of the populations of their nations.[3][4]
Family division
- Iroquoian
- Northern Iroquoian
- (Lake Iroquoian)
- Iroquois Proper (Five Nations)
- Seneca (severely endangered)
- Cayuga (severely endangered)
- Onondaga (severely endangered)
- Susquehannock or Conestoga †
- Mohawk–Oneida
- Oneida (severely endangered)
- Mohawk
- Huronian †
- Huron-Wyandot (severely endangered)
- Petun (Tobacco) †
- Iroquois Proper (Five Nations)
- Tuscarora–Nottoway
- Tuscarora †
- Meherrin †
- Nottoway (severely endangered)
- Unclassified
- Wenrohronon or Wenro †
- Neutral †
- Erie †
- Laurentian †
- Scahentoarrhonon †
- (Lake Iroquoian)
- Southern Iroquoian
- Cherokee
- South Carolina-Georgia dialect (a.k.a. Lower dialect) †
- North Carolina dialect (a.k.a. Middle or Kituwah dialect) (severely endangered)
- Oklahoma dialect (a.k.a. Overhill or Western dialect) (definitely endangered)
- Cherokee
- Northern Iroquoian
† — language extinct/dormant
Evidence is emerging that what has been called the Laurentian language appears to be more than one dialect or language.[5] Ethnographic and linguistic field work with the Wyandot tribal elders (Barbeau 1960) yielded enough documentation for scholars to characterize and classify the Huron and Petun languages.
The languages of the tribes that constituted the tiny Wenrohronon,[lower-alpha 1] The powerful Conestoga Confederacy and the confederations of the Neutral Nation and the Erie Nation are very poorly documented in print. The Huron (Wyandot people) referred to the Neutral people as Atiwandaronk, meaning 'they who understand the language'. The Wenro and Neutral are historically grouped together, and geographically the Wenro's range on the eastern end of Lake Erie placed them between the larger confederations. To the east of the Wenro, beyond the Genesee Gorge, were the lands of the Haudenosaunee Confederacy. To the southeast, beyond the headwaters of the Allegheny River, lay the Conestoga (Susquehannock).[6] The Conestoga Confederacy and Erie were militarily powerful and respected by neighboring tribes.[6] By 1660 all of these peoples but the Conestoga Confederacy and the Haudenosaunee Confederacy were defeated and scattered, migrating to form new tribes or adopted into others. The Iroquoian peoples had a practice of adopting valiant enemies into the tribe; they also adopted captive women and children to replace members who had died.[6]
The group known as the Meherrin were neighbors to the Tuscarora and the Nottoway (Binford 1967) in the American South. They are believed to have spoken an Iroquoian language but documentation is lacking.
External relationships
Attempts to link the Iroquoian, Siouan, and Caddoan languages in a Macro-Siouan family are suggestive but remain unproven (Mithun 1999:305).
Linguistics and language revitalization
As of 2012, a program in Iroquois linguistics at Syracuse University, the Certificate in Iroquois Linguistics for Language Learners, is designed for students and language teachers working in language revitalization.[7][8]
Six Nations Polytechnic in Ohsweken, Ontario offers Ogwehoweh language Diploma and Degree Programs in Mohawk or Cayuga.[9]
Starting in September 2017, the University of Waterloo in Waterloo, Ontario started offering a credit course in Mohawk; the classes are to be given at Renison University College in collaboration with the Waterloo Aboriginal Education Centre, St. Paul's University College.[10]
See also
- Proto-Iroquoian language
- Dean R. Snow and William A. Starna – Archeologists and historians who have conducted ground-breaking archeological research in the Mohawk Valley and other Iroquoian sites.
Notes
References
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Iroquoian". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/iroq1247.
- ↑ Mithun, Marianne. "Grammaticalization and Polysynthesis: Iroquoian". http://www.linguistik.fb05.uni-mainz.de/files/2015/01/Abstract_Mithun.pdf.
- ↑ "UNESCO Interactive Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger". unesco.org. http://www.unesco.org/languages-atlas/index.php?hl=en&page=atlasmap&cc2=US.
- ↑ "Iroquoian Languages". languagegeek.com. 22 February 2008. http://www.languagegeek.com/rotinonhsonni/iroquoian.html.
- ↑ "Laurentian Language and the Laurentian Indian Tribe (Stadaconan, Kwedech, Hochelagan)". http://www.native-languages.org/laurentian.htm.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 Alvin M. Josephy Jr., ed (1961). "The American Heritage Book of Indians". The American Heritage Book of Indians. American Heritage Publishing Co.. pp. 188–219.
- ↑ "Certificate in Iroquois Linguistics for Language Learners". University College. http://uc.syr.edu/CIL/.
- ↑ Gale Courey Toensing (September 2, 2012). "Iroquois Linguistics Certificate at Syracuse University Comes at Important Time for Native Languages". Indian Country Today Media Network. http://indiancountrytodaymedianetwork.com/2012/09/02/iroquois-linguistics-certificate-at-syracuse-university-comes-at-important-time-for-native-languages-132152.
- ↑ "University Program". https://www.snpolytechnic.com/programs-courses/university.
- ↑ Bueckert, Kate (17 Aug 2017). "Mohawk language course to be offered for 1st time at UW". CBC News. http://www.cbc.ca/news/canada/kitchener-waterloo/mohawk-course-kanienkeha-renison-university-waterloo-1.4249770?cmp=rss.
Further reading
Linguistics
- Barbeau, C. Marius (1960), Huron-Wyandot Traditional Narratives in Translations and Native Texts, National Museum of Canada Bulletin 47; Anthropological Series 165, [Ottawa]: Canada Dept. of Northern Affairs and National Resources, OCLC 1990439.
- Binford, Lewis R. (1967), "An Ethnohistory of the Nottoway, Meherrin and Weanock Indians of Southeastern Virginia", Ethnohistory (Ethnohistory, Vol. 14, No. 3/4) 14 (3/4): 103–218, doi:10.2307/480737.
- Chilton, Elizabeth (2004), "Social Complexity in New England: AD 1000–1600", in Pauketat; Loren, Diana Dipaolo, North American Archaeology, Malden, MA: Blackwell Press, pp. 138–60, OCLC 55085697.
- Goddard, Ives, ed. (1996), Handbook of North American Indians, Vol. 17: Languages, Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, ISBN 0-16-048774-9, OCLC 43957746.
- Lounsbury, Floyd G. (1978), "Iroquoian Languages", in Trigger, Bruce G., Handbook of North American Indians, Vol. 15: Northeast, Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution, pp. 334–43 [unified volume Bibliography, pp. 807–90], OCLC 58762737.
- Martin, Scott W. J. (July 2008). "Languages Past and Present: Archaeological Approaches to the Appearance of Northern Iroquoian Speakers in the Lower Great Lakes Region of North America". American Antiquity (Cambridge University Press) 73 (3): 441–463. doi:10.1017/S0002731600046813.
- Mithun, Marianne (1984), "The Proto-Iroquoians: Cultural Reconstruction from Lexical Materials", in Foster, Michael K.; Campisi, Jack; Mithun, Marianne, Extending the Rafters: Interdisciplinary Approaches to Iroquoian Studies, Albany: State University of New York Press, pp. 259–82, ISBN 0-87395-781-4, OCLC 9646457, https://archive.org/details/extendingrafters00fost/page/259.
- Mithun, Marianne (1985), "Untangling the Huron and the Iroquois", International Journal of American Linguistics (University of Chicago Press) 51 (4): 504–7, doi:10.1086/465950.
- Mithun, Marianne (1999), The Languages of Native North America, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-23228-7, OCLC 40467402.
- Rudes, Blair A. (1993), "Iroquoian Vowels", Anthropological Linguistics 37 (1): 16–69.
General works
- Driver, Harold E. 1969. Indians of North America. 2nd edition. University of Chicago Press. ISBN:978-0-226-16467-0
- Ruttenber, Edward Manning. 1992 [1872]. History of the Indian tribes of Hudson's River. Hope Farm Press.
- Snow, Dean R. 1994. The Iroquois. Blackwell Publishers. Peoples of America. ISBN:978-1-55786-225-9
- Snow, Dean R.; Gehring, Charles T; Starna, William A. 1996. In Mohawk country: early narratives about a native people. Syracuse University Press. An anthology of primary sources from 1634 to 1810.
 |


