Social:Old Saxon
| Old Saxon | |
|---|---|
| Old Low German | |
| Sahsisk | |
| Region | Northwest Germany , Northeast Netherlands, Southern Denmark (North Schleswig) |
| Ethnicity | Saxons |
| Era | 8th–12th centuries; mostly developed into Middle Low German at the end of the 12th century |
Indo-European
| |
| Runic, later Latin | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | osx |
osx | |
| Glottolog | olds1250[1] |
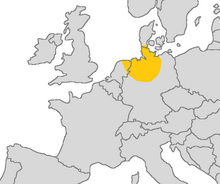 Area in which Old Saxon was spoken in yellow | |
Old Saxon (German: altsächsische Sprache), also known as Old Low German (German: altniederdeutsche Sprache), was a Germanic language and the earliest recorded form of Low German (spoken nowadays in Northern Germany, the northeastern Netherlands, southern Denmark, the Americas and parts of Eastern Europe). It is a West Germanic language, closely related to the Anglo-Frisian languages.[2] It is documented from the 8th century until the 12th century, when it gradually evolved into Middle Low German. It was spoken throughout modern northwestern Germany, primarily in the coastal regions and in the eastern Netherlands by Saxons, a Germanic tribe that inhabited the region of Saxony. It partially shares Anglo-Frisian's (Old Frisian, Old English) Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law which sets it apart from Low Franconian and Irminonic languages, such as Dutch, Luxembourgish and German.
The grammar of Old Saxon was fully inflected with five grammatical cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, and instrumental), three grammatical numbers (singular, plural, and dual), and three grammatical genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter). The dual forms occurred in the first and second persons only.
Characteristics
Relation with other West Germanic languages
In the early Middle Ages, a dialect continuum existed between Old Dutch and Old Saxon, a continuum which has since been interrupted by the simultaneous dissemination of standard languages within each nation and the dissolution of folk dialects. Although they share some features, a number of differences separate Old Saxon, Old English, and Old Dutch. One such difference is the Old Dutch utilization of -a as its plural a-stem noun ending, while Old Saxon and Old English employ -as or -os. However, it seems that Middle Dutch took the Old Saxon a-stem ending from some Middle Low German dialects, as modern Dutch includes the plural ending -s added to certain words. Another difference is the so-called "unified plural": Old Saxon, like Old Frisian and Old English, has one verb form for all three persons in the plural, whereas Old Dutch retained three distinct forms (reduced to two in Middle Dutch).
Old Saxon (or Old Low German) probably evolved primarily from Ingvaeonic dialects in the West Germanic branch of Proto-Germanic in the 5th century. However, Old Saxon, even considered as an Ingvaeonic language, is not a pure Ingvaeonic dialect like Old Frisian and Old English, the latter two sharing some other Ingvaeonic characteristics, which Old Saxon lacked.
Relation to Middle Low German
Old Saxon naturally evolved into Middle Low German over the course of the 11th and 12th centuries, with a great shift from Latin to Low German writing happening around 1150, so that the development of the language can be traced from that period.
The most striking difference between Middle Low German and Old Saxon is in a feature of speech known as vowel reduction, which took place in most other West Germanic languages and some Scandinavian dialects such as Danish, reducing all unstressed vowels to schwa. Thus, such Old Saxon words like gisprekan (spoken) or dagō (days' – gen. pl.) became gesprēken and dāge.
Phonology
Early developments
Old Saxon did not participate in the High German consonant shift, and thus preserves stop consonants p, t, k that have been shifted in Old High German to various fricatives and affricates. The Germanic diphthongs ai, au consistently develop into long vowels ē, ō, whereas in Old High German they appear either as ei, ou or ē, ō depending on the following consonant.
Old Saxon, alone of the West Germanic languages except for Frisian, consistently preserves Germanic /j/ after a consonant, e.g. hēliand "savior" (Template:Lang-goh, Old English: hǣlend, but Template:Lang-got). Germanic umlaut, when it occurs with short a, is inconsistent, e.g. hebbean or habbian "to have" (Old English: habban). This feature was carried over into the descendant-language of Old Saxon, Middle Low German, where e.g. the adjective krank (sick, ill) had the comparative forms krenker and kranker. Apart from the e, however, the umlaut is not marked in writing.
Consonants
The table below lists the consonants of Old Saxon. Phonemes written in parentheses represent allophones and are not independent phonemes.
| Labial | Dental/ Alveolar |
Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nasal | m | n | ||||
| Plosive | voiceless | p | t | k | ||
| voiced | b | d | ɣ (x) | |||
| Fricative | sibilant | s̺ (z) | ||||
| non-sibilant | f (v) | θ (ð) | h | |||
| Approximant | l | j | w | |||
| Rhotic | r | |||||
Notes:
- The voiceless spirants /f/, /θ/, and /s/ gain voiced allophones ([v], [ð], and [z]) when between vowels. This change is only faithfully reflected in writing for [v] (represented with letters such as ⟨ƀ⟩ and ⟨u⟩). The other two allophones continued to be written as before.
- Fricatives were devoiced again word-finally. Beginning in the later Old Saxon period, stops became devoiced word-finally as well.
- Most consonants could be geminated. Notably, geminated /v/ gave /bː/, and geminated /ɣ/ probably gave /ɡː/; Geminated /h/ resulted in /xː/.
- Germanic *h is retained as [x] in these positions and thus merges with devoiced /ɣ/.
Vowels
| Front | Back | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | |||||
| short | long | short | long | short | long | |
| Close | ɪ | iː | (ʏ) | (yː) | ʊ | uː |
| Close-mid | (e) | eː | (øː) | oː | ||
| Open-mid | ɛ | ɛː | (œ) | (œː) | ɔ | ɔː |
| Near-open | (æ) | (æː) | ||||
| Open | ɑ | ɑː | ||||
Notes:
- Long vowels were rare in unstressed syllables and mostly occurred due to suffixation or compounding.
Diphthongs
| Front | ||
|---|---|---|
| Opening | io (ia ie) | |
| Height-harmonic | iu | |
Notes:
- The closing diphthongs /ei/ and /ou/ sometimes occur in texts (especially in Genesis), probably under the influence of Franconian or High German dialects, where they replace Old Saxon developments /ɛː/ and /ɔː/ (which evolved from Proto-Germanic /ai/ and /au/).
- The situation for the front opening diphthongs is somewhat unclear in some texts. Words written with io in the Heliand, the most extensive record of Old Saxon writing, are often found written variably with ia or even ie in most other texts, notably the later ones. The diphthong eventually merges into /eː/ in almost every Middle Low German dialect.
- There also existed 'long' diphthongs /oːu/, /aːu/ and /eːu/. These were, however, treated as two-syllable sequences of a long vowel followed by a short one, not proper diphthongs.
Grammar
Morphology
Unlike modern English, Old Saxon was an inflected language rich in morphological diversity. It kept five out of the six distinct cases of Proto-Germanic: the nominative, accusative, genitive, dative and (Vestigially in the oldest texts) instrumental.
Old Saxon also had three grammatical numbers (singular, and dual, and plural) and three grammatical genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter). The dual forms occurred in the first and second persons only and referred to groups of exactly two.
Nouns
Old Saxon nouns were inflected in very different ways following their classes. Here are the endings for dag, "day" an a-stem masculine noun:
| dag 'day' m. | ||||
| Case | Singular | Plural | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nominative | dag | dagos | ||
| Accusative | dag | dagos | ||
| Genitive | dages, -as | dago | ||
| Dative | dage, -a | dagum, -un | ||
At the end of the Old Saxon period, distinctions between noun classes began to disappear, and endings from one were often transferred to the other declension, and vice versa. This happened to be a large process, and the most common noun classes started to cause the least represented to disappear. As a result, in Middle Low German, only the former weak n-stem and strong a-stem classes remained. These two noun inflection classes started being added to words not only following the historical belonging of this word, but also following the root of the word.
Verbs
The Old Saxon verb inflection system reflects an intermediate stage between Old English and Old Dutch, and further Old High German. Unlike Old High German and Old Dutch, but similarly to Old English, it did not preserve the three different verb endings in the plural, all featured as -ad (also -iad or -iod following the different verb inflection classes). Like Old Dutch, it had only two classes of weak verb, with only a few relic verbs of the third weak class (namely four verbs: libbian, seggian, huggian and hebbian).
This table sums up all seven Old Saxon strong verb classes and the three weak verb classes:
| Strong verbs | Weak verbs | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conjugation | Pronoun | 'to ride' | 'to fly' | 'to help' | 'to break' | 'to speak' | 'to travel' | 'to wield' | 'to deem' | 'to declare' | 'to say' |
| Infinitive | rīdan | fliogan | helpan | brekan | sprekan | faran | waldan | dōmian | mahlon | seggian | |
| Present indicative | |||||||||||
| ik | rīdu | fliugu | hilpu | briku | spriku | faru | waldu | dōmiu | mahlo(n) | seggiu | |
| thū | rīdis | fliugis | hilpis | brikis | sprikis | feris | weldis | dōmis | mahlos | sages | |
| hē/it/siu | rīdid | fliugid | hilpid | brikid | sprikid | ferid | weldid | dōmid | mahlod | saged | |
| wī/gī/sia | rīdad | fliogad | helpad | brekad | sprekad | farad | waldad | dōmiad | mahliod | seggiad | |
| Past indicative | |||||||||||
| ik | rēd | flōg | halp | brak | sprak | fōr | wēld | dōmda | mahloda | sagda | |
| thū | ridi | flugi | hulpi | brāki | sprāki | fōri | wēldi | dōmdes | mahlodes | sagdes | |
| hē/it/siu | rēd | flōg | halp | brak | sprak | fōr | wēld | dōmda | mahloda | sagda | |
| wī/gī/sia | ridun | flugun | hulpun | brākun | sprākun | fōrun | wēldun | dōmdun | mahlodun | sagdun | |
| Present subjunctive | |||||||||||
| ik | rīde | flioge | helpe | breke | spreke | fare | walde | dōmie | mahlo | seggie | |
| thū | rīdes | flioges | helpes | brekes | sprekes | fares | waldes | dōmies | mahlos | seggies | |
| hē/it/siu | rīde | flioge | helpe | breke | spreke | fare | walde | dōmie | mahlo | seggie | |
| wī/gī/sia | rīden | fliogen | helpen | breken | spreken | faren | walden | dōmien | mahlion | seggien | |
| Past subjunctive | |||||||||||
| ik | ridi | flugi | hulpi | brāki | sprāki | fōri | wēldi | dōmdi | mahlodi | sagdi | |
| thū | ridis | flugis | hulpis | brākis | sprākis | fōris | wēldis | dōmdis | mahlodis | sagdis | |
| hē/it/siu | ridi | flugi | hulpi | brāki | sprāki | fōri | wēldi | dōmdi | mahlodi | sagdi | |
| wī/gī/sia | ridin | flugin | hulpin | brākin | sprākin | fōrin | wēldin | dōmdin | mahlodin | sagdin | |
| Imperative | Singular | rīd | fliog | help | brek | sprek | far | wald | dōmi | mahlo | sage |
| Plural | rīdad | fliogad | helpad | brekad | sprekad | farad | waldad | dōmiad | mahliod | seggiad | |
| Present participle | rīdandi | fliogandi | helpandi | brekandi | sprekandi | farandi | waldandi | dōmiandi | mahlondi | seggiandi | |
| Past participle | (gi)ridan | (gi)flogan | (gi)holpan | (gi)brokan | (gi)sprekan | (gi)faran | (gi)waldan | (gi)dōmid | (gi)mahlod | (gi)sagd | |
It should be noticed that the third weak verb class includes only four verbs (namely libbian, seggian, huggian and hebbian); it is a remnant of an older and larger class that was kept in Old High German.
Syntax
Old Saxon syntax is mostly different from that of modern English. Some were simply consequences of the greater level of nominal and verbal inflection – e.g., word order was generally freer. In addition:
- The default word order was verb-second, very close to that of modern Dutch or modern German.
- There was no do-support in questions and negatives.
- Multiple negatives could stack up in a sentence and intensify each other (negative concord), which is not always the case in modern English, modern Dutch, or modern German.
- Sentences with subordinate clauses of the type "when X, Y" (e.g. "When I got home, I ate dinner.") did not use a wh-type conjunction, but rather used a th-type correlative conjunction (e.g. thô X, thô Y in place of "when X, Y"). The wh-type conjunctions were used only as interrogative pronouns and indefinite pronouns.
- Similarly, wh- forms were not used as relative pronouns (as in "the man who saw me" or "the car which I bought"). Instead, an indeclinable word the was used, often in conjunction with the definite article (which was declined for case, number and gender).
Orthography
Old Saxon comes down in a number of different manuscripts whose spelling systems sometimes differ markedly. In this section, only the letters used in normalized versions of the Heliand will be kept, and the sounds modern scholars have traditionally assigned to these letters. Where spelling deviations in other texts may point to significant pronunciation variants, this will be indicated.
In general, the spelling of Old Saxon corresponds quite well to that of the other ancient Germanic languages, such as Old High German or Gothic.
- c and k were both used for [k]. However, it seems that, as in other West-Germanic dialects, when [k] was followed by i or e, it had the pronunciation /ts/ or /kʲsʲ/.[3] The letters c and x were preferred for the palatalisations, k and even sometimes ch being rather used before u, o or a for /k/ (kuning for [kʏnɪŋk] 'king', modern köning ; crûci for [kryːtsi] ; forsachistu for [forsakistuː]).
- g represented [ɣ] or its allophone [ɡ]: brengian [brɛŋɡjan] 'to bring', seggian [sɛɡɡjan] 'to say', wege [wɛɣe] 'way' (dative).
- g seems, at least in a few dialects, to have had the pronunciation [j] or [ʝ] at the beginning of a word, only when followed by i or e. Thus we find giār [jaːr] 'year' and even gēr [jeːr] 'year', the latter betraying a strong Old Frisian influence.
- h represents [h] and its allophone [x]: holt [hɔlt] 'wood', naht [naxt] 'night' (mod. nacht).
- i is used for both the vowels [ɪ] and [iː] and the consonant [j]: ik [ɪk] 'I' (mod. ick, ik), iār [jaːr] 'year'.
- qu and kw always represent [kw]: quāmun [kwaːmʊn] 'they came'.
- s represented [s], and between two vowels also [z].
- th is used to indicate [θ]: thōhtun [θoːxtun] 'they thought'. ð is used for [ð], occasionally also written dh.
- u represented the vowels [ʊ] and [uː], or the consonant [β] ~ [v], which was denoted sporadically across manuscripts by either ⟨ƀ⟩, ⟨b⟩, ⟨u⟩, ⟨v⟩, or ⟨f⟩'.[4]
- uu was normally used to represent [w], predating the letter w.
- z only appeared in a few texts due to Old High German influence.
Literature
Only a few texts survive, predominantly baptismal vows the Saxons were required to perform at the behest of Charlemagne. The only literary texts preserved are Heliand and fragments of the Old Saxon Genesis. There is also:
- Beda homily (Homilie Bedas)
- Credo (Abrenunciatio diaboli et credo) → Old Saxon baptismal vow.
- Essener Heberegister
- Old Saxon Baptismal Vow (German: Sächsisches Taufgelöbnis)
- Penitentiary (altsächsische Beichte, altwestfälische Beichte)
- Trierer Blutsegen (
 de.)
de.) - Spurihalz (Wiener Pferdsegen) (
 de.)
de.) - Wurmsegen (Wiener Wurmsegen) (
 de).
de). - Psalms commentary (Gernroder Psalmenkommentar)
Text sample
A poetic version of the Lord's Prayer in the form of the traditional Germanic alliterative verse is given in Old Saxon below as it appears in the Heliand.
| Line | Original | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| [1] | Fadar usa firiho barno, | Father our [our Father/Father of us], men's sons [the sons of men], |
| [2] | thu bist an them hohon himila rikea, | Thou art [You are] in the high heavenly domain [kingdom of the heavens], |
| [3] | geuuihid si thin namo uuordo gehuuilico, | Hallowed be Thy [Your] name (with) every word, |
| [4] | Cuma thin craftag riki. | May Thy [Your] mighty domain [kingdom] come. |
| [5] | UUerða thin uuilleo oƀar thesa werold alla, | Worth [May] Thy [Your] will (be done) over all this world, |
| [6] | so sama an erðo, so thar uppa ist | Just the same on earth, as (it) is up there |
| [7] | an them hohon himilo rikea. | in the high heavenly domain [kingdom of the heavens]. |
| [8] | Gef us dag gehuuilikes rad, drohtin the godo, | Give us every day rede [advice/counsel], (oh) Drighten [Lord] the Good, |
| [9] | thina helaga helpa, endi alat us, heƀenes uuard, | (and) Thy [Your] holy help, and deliver [set free/absolve] us, (oh) Heaven's Ward [Lord/Ruler of Heaven], |
| [10] | managoro mensculdio, | (of our) many crimes, |
| [11] | al so uue oðrum mannum doan. | just as we (shall) do (to) other men [people]. |
| [12] | Ne lat us farledean leða uuihti | Do not let loath(some) wights forlead [mislead, seduce] us |
| [13] | so forð an iro uuilleon, so uui uuirðige sind, | so forth in [to go on with] their will, so [given that] we are worthy, |
| [14] | ac help us uuiðar allun uƀilon dadiun. | but (rather) help us wither [against] all evil deeds. |
See also
- Old Saxon Genesis
- Old Saxon Baptismal Vow
- Heliand
- Middle Low German
- Low German
- Ingvaeonic nasal spirant law
Notes
- ↑ Hammarström, Harald; Forkel, Robert; Haspelmath, Martin, eds (2017). "Old Saxon". Glottolog 3.0. Jena, Germany: Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History. http://glottolog.org/resource/languoid/id/olds1250.
- ↑ "Old Saxon language | Old Saxon language | West Germanic, Low German | Britannica" (in en). https://www.britannica.com/topic/Old-Saxon-language.
- ↑ Lasch 1914, §339
- ↑ Altsächsische Grammatik. pp. 126–128, 161.
Bibliography
Sources
- Galleé, Johan Hendrik (1910). Altsächsische Grammatik. Halle: Max Niemeyer.
- Lasch, Agathe (1914). Mittelniederdeutsche Grammatik. Halle: Max Niemeyer. https://archive.org/details/mittelniederdeu00lasc.
General
- Euler, Wolfram (2013). Das Westgermanische – von der Herausbildung im 3. bis zur Aufgliederung im 7. Jahrhundert – Analyse und Rekonstruktion (West Germanic – from its Emergence in the 3rd up until its Dissolution in the 7th Century CE – Analyses and Reconstruction). 244 p., in German with English summary, London/Berlin 2013, ISBN:978-3-9812110-7-8.
- Rauch, Irmengard (1992). The Old Saxon Language. Berkeley Models of Grammar: Peter Lang Publishing.
- Ringe, Donald R. and Taylor, Ann (2014). The Development of Old English – A Linguistic History of English, vol. II, 632p. ISBN:978-0199207848. Oxford.
- Holthausen, Ferdinand (1923). Altsächsisches Elementarbuch. Ulan Press.
Lexicons
- Tiefenbach, Heinrich (2010). Altsächsisches Handwörterbuch / A Concise Old Saxon Dictionary. De Gruyter.
- Gerhard Köbler: Altsächsisches Wörterbuch, (5. Auflage) 2014. ("An Old Saxon Dictionary")
External history
- Robinson, Orrin W. (1947). Old English and its closest relatives. Stanford: Stanford University Press.
- Helfenstein, Jacob (1901). Comparative Grammar of the Teutonic languages. Oxford: Forgotten Books.
- Meidinger, Heinrich (1923). Vergleichendes Etymologisches Wörterbuch Der Gothisch-Teutonischen Mundarten. Ulan Press.
- Schade, Oskar (1923). Altdeutsches Lesebuch. Ulan Press.
- Ammon, Hermann (1922). Repetitorium der deutschen sprache, gotisch, althochdeutsch, altsächsisch. Michigan: University of Michigan Library.
External links
- Einführung in das Altsächsische (An Introduction to Old Saxon) by Roland Schuhmann (in German); copy at the Internet Archive
- Galleé, Johan Hendrik (1910). Altsächsische Grammatik. Halle: Max Niemeyer. (at the Internet Archive)
 |


