Chemistry:ADH-1
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Exherin |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
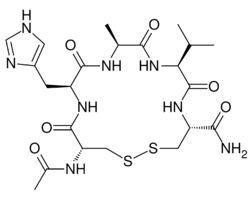
| Formula | C22H34N8O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 570.68 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
ADH-1 (brand name Exherin) is a small, cyclic pentapeptide vascular-targeting drug. It was developed by Adherex Technologies.
ADH-1 selectively and competitively binds to and blocks N-cadherin, which may result in disruption of tumor vasculature, inhibition of tumor cell growth, and the induction of tumor cell and endothelial cell apoptosis.[1] N-cadherin, a cell- surface transmembrane glycoprotein of the cadherin superfamily of proteins involved in calcium-mediated cell–cell adhesion and signaling mechanisms;[1] may be upregulated in some aggressive tumors and the endothelial cells and pericytes of some tumor blood vessels.[1]
In 2006, Adherex and NCI formed a clinical trial agreement stating that NCI will sponsor clinical trials of ADH-1 in a variety of cancer types. ADH-1 received orphan drug status from the FDA in 2008.[2]
In a pilot study (phase I trial), ADH-1 intravenous pretreatment before chemotherapy in metastatic melanoma completely destroyed tumors in half of patients. It is being investigated in phase II trials for advanced extremity melanoma.[3][4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 "ADH-1". NCI Drug Dictionary. 2011-02-02. http://www.cancer.gov/Templates/drugdictionary.aspx?CdrID=462569.
- ↑ "ADH-1". http://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800014745. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ↑ "Phase I clinical trial of Exherin (ADH-1) in patients with advanced solid tumors". Curr Clin Pharmacol 8 (1): 81–88. Feb 1, 2013. PMID 22280327.
- ↑ Physorg:Drug combination may be effective against deadly melanoma, pilot study shows
 |

