Chemistry:SIB-1757
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
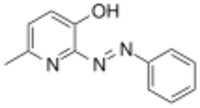 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C12H11N3O |
| Molar mass | 213.240 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
SIB-1757 is a drug used in scientific research which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5.[1] It has anti-hyperalgesia effects in animals.[2] SIB-1757 along with other mGluR5 antagonists has been shown to have neuroprotective and hepatoprotective effects,[3][4] and it is also used to study the role of the mGluR5 receptor in brain development.[5]
References
- ↑ "SIB-1757 and SIB-1893: selective, noncompetitive antagonists of metabotropic glutamate receptor type 5". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 290 (1): 170–81. July 1999. PMID 10381773.
- ↑ "Peripheral and spinal antihyperalgesic activity of SIB-1757, a metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGLUR(5)) antagonist, in experimental neuropathic pain in rats". Neuroscience Letters 292 (2): 115–8. October 2000. doi:10.1016/S0304-3940(00)01458-0. PMID 10998562.
- ↑ "Selective blockade of mGlu5 metabotropic glutamate receptors is protective against acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in mice". Journal of Hepatology 38 (2): 179–87. February 2003. doi:10.1016/S0168-8278(02)00384-7. PMID 12547406.
- ↑ "Characterisation of the actions of group I metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype selective ligands on excitatory amino acid release and sodium-dependent re-uptake in rat cerebrocortical minislices". Journal of Neurochemistry 86 (6): 1346–58. September 2003. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01932.x. PMID 12950444.
- ↑ "Modulatory action of metabotropic glutamate receptor (mGluR) 5 on mGluR1 function in striatal cholinergic interneurons". Neuropharmacology. 49 Suppl 1: 104–13. 2005. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.05.012. PMID 16005029.
 |

