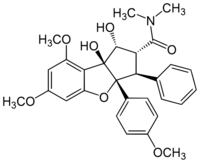
Chemistry:Rocaglamide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(1R,2R,3S,3aR,8bS)-1,8b-Dihydroxy-6,8-dimethoxy-3a-(4-methoxyphenyl)-N,N-dimethyl-3-phenyl-2,3,3a,8b-tetrahydro-1H-cyclopenta[b][1]benzofuran-2-carboxamide | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C29H31NO7 | |
| Molar mass | 505.567 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Rocaglamide is a natural product which belongs to a class of molecules called flavaglines.[1][2] This compound was isolated in 1982 by King, Ming-Lu (金明儒) and colleagues based on its antileukemic activity.[3] The name of Rocaglamide is named from two parts: Roc- and aglamide. Roc- means Republic of China (中華民國), the place in which this product isolated; aglamide indicates this product is isolated from Large-leaved Aglaia (Scientific name: Aglaia rimosa[4]). Like other flavaglines, rocaglamide displays potent insecticidal, antifungal, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities. Rocaglamide A (RocA) inhibits eukaryotic translation initiation by binding to the translation initiation factor eIF4A and converting it into a translational repressor.[5]
Rocaglamide was first synthesized by Barry Trost in 1990.[6] Although other syntheses have been described since, Trost’s remains the only one to afford rocaglamide in an enantio-specific manner.
See also
References
- ↑ "Chemistry and biology of rocaglamides (= flavaglines) and related derivatives from aglaia species (meliaceae)". Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products. Fortschritte der Chemie organischer Naturstoffe / Progress in the Chemistry of Organic Natural Products 94: 1–58. 2011. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-0748-5_1. ISBN 978-3-7091-0747-8. PMID 21833837.
- ↑ "Recent advances in the biology and chemistry of the flavaglines". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 20 (6): 1857–64. March 2012. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2011.10.048. PMID 22071525.
- ↑ "X-Ray crystal structure of rocaglamide, a novel antileukemic 1H-cyclopenta[b]benzofuran from Aglaia elliptifolia". Chem. Commun. (20): 1150–1. 1992. doi:10.1039/c39820001150.
- ↑ "Aglaia rimosa (Blanco) Merr." (in en). Plants of the World Online. https://powo.science.kew.org/taxon/urn:lsid:ipni.org:names:577291-1. Retrieved 2022-12-14.
- ↑ "Rocaglates convert DEAD-box protein eIF4A into a sequence-selective translational repressor". Nature 534 (7608): 558–61. June 2016. doi:10.1038/nature17978. PMID 27309803. Bibcode: 2016Natur.534..558I.
- ↑ "An unusual oxidative cyclization. A synthesis and absolute stereochemical assignment of (−)-rocaglamide". Journal of the American Chemical Society 112 (24): 9022–4. November 1990. doi:10.1021/ja00180a081.
 |

