Chemistry:Tris(glycinato)cobalt(III)
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Other names
cobalt(III) glycinate
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Appearance | violet or reddish solids |
| 0.199 g/L (red isomer, 25 °C), 9.33 g/L (violet, 25 °C)[1] | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
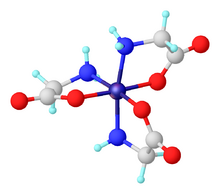
Tris(glycinato)cobalt(III) describes coordination complexes with the formula Co(H
2NCH
2CO
2)
3. Several isomers exist of these octahedral complexes formed between low-spin d6 Co(III) and the conjugate base of the amino acid glycine.
Structures
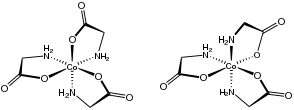
Both a meridional isomer and a facial isomer are known. In the former the Co-O bonds share a plane, and in the facial isomer they do not. Each of these two isomers exists also as pairs of stereoisomers, termed Δ and Λ. This set of compounds are prototypes of many tris(aminocarboxylate) complexes, with the notable distinction that the Co(III) derivatives do not isomerize readily and can thus be separated.
The violet isomer is obtained anhydrous, whereas the red derivative is the monohydrate.[1] X-ray crystallographic characterization of the mer isomer demonstrates the existence of a dihydrate, however.[2]
Synthesis
The reaction of glycine with sodium tris(carbonato)cobalt(III) produces both the violet meridional and red-pink facial isomers in approximately equal amounts. The compounds are separated by fractional crystallization.[1] These complexes have been characterized by X-ray crystallography.[3]
The isomeric forms of tris(glycinato)cobalt(III) are poorly soluble in water. The solubility increases considerably in acidic solution.
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kauffman, George B.; Karbassi, Mohammad; Kyuno, Eishin (1989). "Tris(glycinato)cobalt(III)". Inorganic Syntheses 25: 135–139. doi:10.1002/9780470132562.ch32. ISBN 9780470132562.
- ↑ Dewan, J. C. (1988). "Structure of Tris(glycinato)cobalt(III) Dihydrate". Acta Crystallographica Section C Crystal Structure Communications 44 (12): 2199–2201. doi:10.1107/S0108270188009126.
- ↑ Yu, K.-Q.; Sun, Y.-X.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, N.-W.; Che, H.-W. (2007). "Tris(glycinato-κ2N,O)cobalt(III)". Acta Crystallogr E63: m740–m742. doi:10.1107/S1600536807005636.
 |