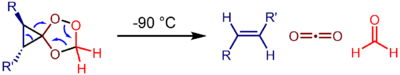Chemistry:Coarctate reaction
A coarctate reaction is a concerted reaction whose transition state involves two rings, in which at least one atom undergoes the simultaneous making and breaking of two bonds. It is an uncommon reaction topology, compared with linear topology and pericyclic topology (itself subdivided into Hückel and Möbius topologies). The name is derived from the Latin coarctare, meaning 'to constrict'.
Transition state topologies
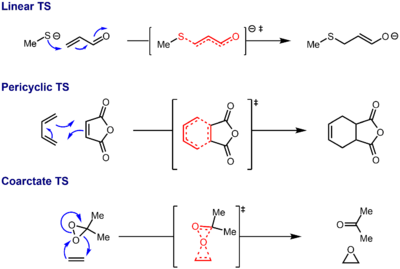
Reactions of linear topology are the most common, and consist of all transformations whose transition states are acyclic, including addition, elimination, substitution, and (some types of) fragmentation reactions. By contrast, in pericyclic reactions, the atoms under chemical change form a single closed cycle, and include reactions like the Diels–Alder reaction and Cope rearrangement, among many others.
In contrast to these types of reactions, a coarctate reaction is characterized by a doubly cyclic transition state, in which at least one atom undergoes the simultaneous making and breaking of two bonds. Thus, the topology of the transition state of a coarctate reaction is a constricted cycle that meets with itself (resembling a figure eight) while the topology of pericyclic and linear reactions are a circle (or Möbius strip) and line segment, respectively. The concept was first proposed by Rainer Herges.[1][2]
Examples
The most well-known example of a coarctate transition state is that of the epoxidation of an olefin by dimethyldioxirane.[3] In this transition state, the oxygen atom transferred to the olefin forms a cycle with the acetone leaving group and a cycle with the olefin undergoing epoxidation. Another well-studied reaction is the fragmentation of spirocyclic ozonides into formaldehyde, CO2, and an olefin.
Selection rules, resembling the Woodward-Hoffmann rules, have been proposed to explain patterns in reaction activation energy related to transition state topology or orbital symmetry.[4]
References
- ↑ Herges, Rainer (1994-01-01). "Coarctate transition states: the discovery of a reaction principle". Journal of Chemical Information and Computer Sciences 34 (1): 91–102. doi:10.1021/ci00017a011. ISSN 0095-2338.
- ↑ Herges, Rainer (1994-02-18). "Organizing Principle of Complex Reactions and Theory of Coarctate Transition States" (in en). Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English 33 (3): 255–276. doi:10.1002/anie.199402551. ISSN 1521-3773.
- ↑ Formally, the "butterfly mechanism" of peracid epoxidation is also coarctate. However, the 1s orbital associated with the hydrogen atom cannot undergo productive overlap as a result of its symmetry (see Herges, 2015). Therefore, the orbital symmetry rules developed for coarctate reactions do not apply. This type of reaction is known as a "pseudocoarctate", in analogy to pseudopericyclic reactions.
- ↑ Herges, Rainer (2015). "Coarctate and Pseudocoarctate Reactions: Stereochemical Rules". The Journal of Organic Chemistry 80 (23): 11869–11876. doi:10.1021/acs.joc.5b01959. PMID 26421714.
 |