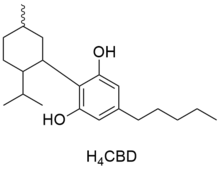
Chemistry:H4-CBD
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-(2-Isopropyl-5-methylcyclohexyl)-5-pentylbenzene-1,3-diol
| |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H34O2 | |
| Molar mass | 318.501 g·mol−1 |
| Related compounds | |
Related compounds
|
H2-CBD |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
H4CBD (hydrogenated CBD, tetrahydrocannabidiol) is a cannabinoid that was first synthesized by the Todd group[clarification needed] in 1940 derived from the catalytic hydrogenation of cannabidiol.[1]
H2-CBD and 8,9-dihydrocannabidiol have also been referred to as "hydrogenated CBD", which may cause confusion.
Pharmacology
In 2006, it was discovered that H4CBD has a binding affinity of 145 nM at the CB1 receptor and potential anti-inflammatory effects independent of its cannabinoid receptor action.[2] In contrast, CBD has been found to bind to the CB1 receptor as an inverse agonist/antagonist with a Ki ranging from 3.3 to 4.8 mM.[3]
Elucidation
In 2023 H4CBD epimers were elucidated using NOESY and COSY NMR spectroscopic techniques, while the inclusion of LC-MS and SCFC were used to isolate individual diasteromers.[4]
See also
- H2-CBD (also hydrogenated CBD)
- 8,9-Dihydrocannabidiol (one of the two components in H2CBD)
- Hexahydrocannabinol (hydrogenated THC)
- 4'-Fluorocannabidiol
- 7-Hydroxycannabidiol
- Abnormal cannabidiol
- Cannabidiol dimethyl ether
- Delta-6-cannabidiol
References
- ↑ Jacob, A.; Todd, A. R. (1940). "119. Cannabis indica. Part II. Isolation of cannabidiol from Egyptian hashish. Observations on the structure of cannabinol". J. Chem. Soc. 119: 649–653. doi:10.1039/jr9400000649.
- ↑ Ben-Shabat, Shimon; Hanuš, Lumír O.; Katzavian, Galia; Gallily, Ruth (February 2006). "New Cannabidiol Derivatives: Synthesis, Binding to Cannabinoid Receptor, and Evaluation of Their Antiinflammatory Activity". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 49 (3): 1113–1117. doi:10.1021/jm050709m. PMID 16451075. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jm050709m.
- ↑ "A narrative review of molecular mechanism and therapeutic effect of cannabidiol (CBD)". Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. January 2022. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/bcpt.13710.
- ↑ Collins, Arianna; Ramirez, Giovanni; Tesfatsion, Tesfay; Ray, Kyle P; Caudill, Scott; Cruces, Westley (March 2023). "Synthesis and Characterization of the Diastereomers of HHC and H4CBD". Natural Product Communications 18 (3): 1934578X2311589. doi:10.1177/1934578x231158910.
 |

