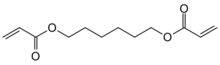
Chemistry:1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Hexane-1,6-diyl di(prop-2-enoate) | |
| Other names
HDDA, HDODA
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 3082 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H18O4 | |
| Molar mass | 226.27 g/mol |
| Appearance | colorless oil |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms | 
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H315, H317, H319 | |
| P261, P264, P272, P280, P302+352, P305+351+338, P321, P332+313, P333+313, P337+313, P362, P363, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate (HDDA or HDODA) is a difunctional acrylate ester monomer used in the manufacture of polymers.[1][2] It is particularly useful for use in ultraviolet light cure applications.[3] Furthermore, it is also used in adhesives, sealants, alkyd coatings, elastomers, photopolymers, and inks for improved adhesion, hardness, abrasion and heat resistance.[4] Like other acrylate monomers it is usually supplied with a radical inhibitor such as hydroquinone added.[5]
Preparation
The material is prepared by acid-catalyzed esterification of 1,6-hexanediol with acrylic acid.[6]
Other uses
As the molecule has acrylic functionality, it is capable of undergoing the Michael reaction with an amine. This allows it use in epoxy chemistry where its use speeds up the cure time considerably.[7]
See also
- TMPTA (trimethylolpropane triacrylate), a triacrylate crosslinker
- Pentaerythritol tetraacrylate, a tetraacrylate crosslinker
References
- ↑ PubChem. "1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate" (in en). https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/25644.
- ↑ "1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate | C12H18O4 | ChemSpider". http://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.23890.html.
- ↑ Ajiboye, Gbenga (2012). "Industrially relevant epoxy-acrylate hybrid resin photopolymerizations". https://ir.uiowa.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=3559&context=etd.
- ↑ Abrasion Resistance Testing-Vehicle Exterior Graphics and Pin Striping, SAE International, doi:10.4271/j1847_198906
- ↑ "13048-33-4 - 1,6-Hexanediol diacrylate, 99% (reactive esters), stab. with 90ppm hydroquinone - HDODA - 43203 - Alfa Aesar". https://www.alfa.com/en/catalog/043203/.
- ↑ Ohara, Takashi; Sato, Takahisa; Shimizu, Noboru; Prescher, Günter; Schwind, Helmut; Weiberg, Otto; Marten, Klaus; Greim, Helmut (2003). "Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a01_161.pub2.
- ↑ "Epoxy Polyacrylate Resins". https://www.hexion.com/en-us/chemistry/epoxy-resins-curing-agents-modifiers/multi-functional-and-specialty-resins/epoxy-polyacrylates.
External links
 |

