Chemistry:Methoxymethanol
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
Methoxymethanol | |
| Other names
Formaldehyde methyl hemiacetal
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 1900186 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C2H6O2 | |
| Molar mass | 62.068 g·mol−1 |
| Density | 0.948 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |   
|
| GHS Signal word | Warning |
| H226, H302, H371 | |
| P210, P233, P240, P241, P242, P243, P260, P264, P270, P280, P301+312, P303+361+353, P309+311, P330, P370+378, P403+235, P405, P501 | |
| Flash point | 39.9 °C (103.8 °F; 313.0 K) |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
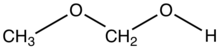
Methoxymethanol is a chemical compound which is both an ether and an alcohol, a hemiformal.[1] The structural formula can be written as CH3OCH2OH. It has been discovered in space.[2]
Formation
Methoxymethanol forms spontaneously when a water solution of formaldehyde and methanol are mixed.[3][1] or when formaldehyde is bubbled through methanol.[4]
In space methoxymethanol can form when methanol radicals (CH2OH or CH3O) react. These are radiolysis products derived when ultraviolet light or cosmic rays hit frozen methanol.[3]
Methanol can react with carbon dioxide and hydrogen at 80°C and some pressure with a ruthenium or cobalt catalyst, to yield some methoxymethanol.[5]
Properties
Different conformations of the molecule are Gauche-gauce (Gg), Gauche-gauce' (Gg'), and Trans-gauche (Tg).[6]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Maiwald, Michael; Fischer, Holger H.; Ott, Michael; Peschla, Roger; Kuhnert, Christian; Kreiter, Cornelius G.; Maurer, Gerd; Hasse, Hans (January 2003). "Quantitative NMR Spectroscopy of Complex Liquid Mixtures: Methods and Results for Chemical Equilibria in Formaldehyde−Water−Methanol at Temperatures up to 383 K". Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research 42 (2): 259–266. doi:10.1021/ie0203072.
- ↑ McGuire, Brett A.; Shingledecker, Christopher N.; Willis, Eric R.; Burkhardt, Andrew M.; El-Abd, Samer; Motiyenko, Roman A.; Brogan, Crystal L.; Hunter, Todd R. et al. (2017). "ALMA Detection of Interstellar Methoxymethanol (CH3OCH2OH)" (in en). The Astrophysical Journal 851 (2): L46. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/aaa0c3. Bibcode: 2017ApJ...851L..46M.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Hays, Brian M.; Widicus Weaver, Susanna L. (6 May 2013). "Theoretical Examination of O(1D) Insertion Reactions to Form Methanediol, Methoxymethanol, and Aminomethanol". The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 117 (32): 7142–7148. doi:10.1021/jp400753r. PMID 23646865. Bibcode: 2013JPCA..117.7142H.
- ↑ Celik, Fuat E.; Lawrence, Henry; Bell, Alexis T. (June 2008). "Synthesis of precursors to ethylene glycol from formaldehyde and methyl formate catalyzed by heteropoly acids". Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical 288 (1–2): 87–96. doi:10.1016/j.molcata.2008.03.029.
- ↑ Dixneuf, Pierre H.; Soulé, Jean-François (2019) (in en). Organometallics for Green Catalysis. Springer. pp. 69–70. ISBN 978-3-030-10955-4. https://books.google.com/books?id=IB2KDwAAQBAJ&pg=PA70.
- ↑ Motiyenko, R. A. (21 June 2016). "Millimeter-wave spectroscopy of methoxymethanol" (in en). 71st International Symposium on Molecular Spectroscopy: 1. doi:10.15278/isms.2016.TH04. ISBN 978-1-5330-5390-9. Bibcode: 2016isms.confETH04M. https://hdl.handle.net/2142/91121.
 |

