Chemistry:Phthalimidoperoxycaproic acid
From HandWiki
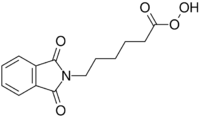
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
6-(1,3-Dioxo-1,3-dihydro-2H-isoindol-2-yl)hexaneperoxoic acid | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H15NO5 | |
| Molar mass | 277.276 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| GHS pictograms |    [1] [1]
|
| GHS Signal word | Danger |
| H242, H318, H400 | |
| P210, P220, P234, P273, P280, P305+351+338, P310, P370+378, P391, P403+235, P411, P420, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Phthalimidoperoxycaproic acid (ε- or 6-(phthalimido)peroxyhexanoic acid, abbreviated as PAP) is a synthetic organic peroxy acid derived from caprolactam and phthalic anhydride.[2] The compound is mainly used as a preformed bleaching agent, alternatively to or together with hydrogen peroxide, in moderate laundry conditions of pH and temperature.[2] It is also used as a tooth whitening agent.[3] PAP is a white odorless crystalline powder at room temperature. It is slightly soluble in water and a strong oxidizer.[2][4]
References
- ↑ CID 9860421 from PubChem
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Zoller, Uri (2008-10-29) (in en). Handbook of Detergents, Part E: Applications. CRC Press. pp. 378–379. ISBN 9781420018165. https://books.google.com/books?id=2mrLBQAAQBAJ.
- ↑ Bizhang, Mozhgan; Domin, Julia; Danesh, Gholamreza; Zimmer, Stefan (2017). "Effectiveness of a new non-hydrogen peroxide bleaching agent after single use - a double-blind placebo-controlled short-term study". Journal of Applied Oral Science 25 (5): 575–584. doi:10.1590/1678-7757-2016-0463. ISSN 1678-7757. PMID 29069156.
- ↑ "Crystalline forms of imidoalkanpercarboxylic acids" EP patent 1523474, issued 2003-07-08
 |

