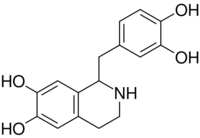
Chemistry:Tetrahydropapaveroline
From HandWiki
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)methyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline-6,7-diol
| |
| Other names
Norlaudanosoline; Tetrahydroxypapaveroline
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C16H17NO4 | |
| Molar mass | 287.315 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Tetrahydropapaveroline (norlaudanosoline) is a benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid.[1]
It can be formed in trace amounts in the brain by a condensation reaction of dopamine and dopaldehyde (a metabolite of dopamine).[1][2]
It inhibits dopamine uptake within the cerebral cortex.[citation needed]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Richter, Derek (14 October 2016) (in en). Addiction and Brain Damage. Routledge. p. 24. ISBN 978-1-315-45403-0. https://books.google.com/books?id=6MNCDQAAQBAJ&pg=PT24.
- ↑ RD Myers; CL Melchior (29 Apr 1977). "Alcohol drinking: abnormal intake caused by tetrahydropapaveroline in brain". Science 196 (4289): 554–556. doi:10.1126/science.557839. PMID 557839. Bibcode: 1977Sci...196..554M.
 |

