Chemistry:Meclinertant
From HandWiki
Short description: Chemical compound
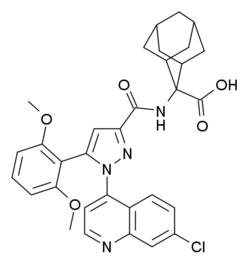 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H31ClN4O5 |
| Molar mass | 587.064 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| (verify) | |
Meclinertant (SR-48692) is a drug which acts as a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the neurotensin receptor NTS1, and was the first non-peptide antagonist developed for this receptor.[1][2] It is used in scientific research to explore the interaction between neurotensin and other neurotransmitters in the brain,[3][4][5][6][7][8] and produces anxiolytic, anti-addictive and memory-impairing effects in animal studies.[9][10][11][12]
References
- ↑ "Biochemical and pharmacological profile of a potent and selective nonpeptide antagonist of the neurotensin receptor". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 90 (1): 65–9. January 1993. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.1.65. PMID 8380498.
- ↑ "Neuropharmacological profile of non-peptide neurotensin antagonists". Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 9 (6): 513–21. 1995. doi:10.1111/j.1472-8206.1995.tb00528.x. PMID 8808171.
- ↑ "Use of nonpeptide antagonists to explore the physiological roles of neurotensin. Focus on brain neurotensin/dopamine interactions". Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 814: 125–41. April 1997. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1997.tb46151.x. PMID 9160965.
- ↑ "Neurotensin and the serotonergic system". Progress in Neurobiology 52 (6): 455–68. August 1997. doi:10.1016/S0301-0082(97)00025-7. PMID 9316156.
- ↑ "Neurotensin: dual roles in psychostimulant and antipsychotic drug responses". Life Sciences 73 (6): 801–11. June 2003. doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00411-9. PMID 12801600.
- ↑ "Neurotensin selectively facilitates glutamatergic transmission in globus pallidus". Neuroscience 141 (4): 1871–8. September 2006. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.05.049. PMID 16814931.
- ↑ "Neurotensin modulation of acetylcholine, GABA, and aspartate release from rat prefrontal cortex studied in vivo with microdialysis". Brain Research Bulletin 77 (2–3): 129–35. September 2008. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2008.04.003. PMID 18721670.
- ↑ "Stimulation by neurotensin of dopamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) release from rat prefrontal cortex: possible role of NTR1 receptors in neuropsychiatric disorders". Neurochemistry International 53 (6–8): 355–61. December 2008. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2008.08.010. PMID 18835308.
- ↑ "Characterization of the profile of neurokinin-2 and neurotensin receptor antagonists in the mouse defense test battery". Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews 25 (7–8): 619–26. December 2001. doi:10.1016/S0149-7634(01)00045-8. PMID 11801287.
- ↑ "Microinfusions of neurotensin antagonist SR 48692 within the nucleus accumbens core impair spatial learning in rats". Behavioral Neuroscience 120 (5): 1093–102. October 2006. doi:10.1037/0735-7044.120.5.1093. PMID 17014260.
- ↑ "Neurotensin receptor antagonist administered during cocaine withdrawal decreases locomotor sensitization and conditioned place preference". Neuropsychopharmacology 32 (12): 2601–10. December 2007. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301382. PMID 17356568.
- ↑ "Evidence for a role of endogenous neurotensin in the development of sensitization to the locomotor stimulant effect of morphine". European Journal of Pharmacology 594 (1–3): 132–8. October 2008. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2008.07.048. PMID 18706409.
External links
 |

