Chemistry:Boletocrocin
From HandWiki
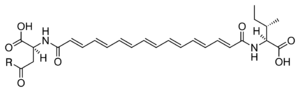
General structure. If R = OH (aspartic acid), boletocrocin A; R = NH2 (asparagine), boletocrocin B.
Boletocrocin is any one of a group of seven closely related organic compounds, individually named boletocrocin A through boletrocrocin G.[1] These compounds are polyene dicarboxylic acids that include both lipophilic and polar amino acids.[2] They were extracted from the brightly colored mushrooms Boletus laetissimus and B. rufoaureus.[2] The boletocrocins' conjugated systems account for the intense color.
Related biological pigments are present in other fungi, such as calostomal (from Calostoma cinnabarinum),[3] melanocrocin (from Melanogaster broomeianus),[4] and mycenaaruin A (from Mycena aurantiomarginata).[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Mycenaaurin A, an Antibacterial Polyene Pigment from the Fruiting Bodies of Mycena aurantiomarginata". Journal of Natural Products 73 (8): 1350–1354. 2010. doi:10.1021/np100155z. PMID 20617819.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 "Polyene pigments from fruit-bodies of boletus laetissimus and B. rufo-aureus (basidiomycetes)". Phytochemistry 49 (6): 1693–1697. 1998. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00319-7. PMID 11711083.
- ↑ "Calostomal, a polyene pigment from the gasteromycete Calostoma cinnabarinum (Boletales)". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung B 62 (1): 129–131. 2007. doi:10.1515/znb-2007-0120. http://www.znaturforsch.com/ab/v62b/s62b0129.pdf.
- ↑ "Melanocrocin, a polyene pigment from Melanogaster broomeianus (Basidiomycetes)". Zeitschrift für Naturforschung C 56 (7–8): 495–498. 2001. doi:10.1515/znc-2001-7-803. PMID 11531079.
 |

