Chemistry:Rubrocurcumin
From HandWiki
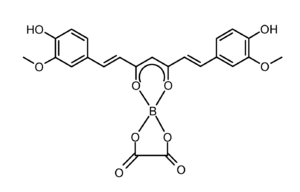
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2-[(1E,3Z,6E)-1,7-bis(4-hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl)-5-oxohepta-1,3,6-trien-3-yl]oxy-1,3,2-dioxaborolane-4,5-dione
| |
| Other names
Rubrocurcumin
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C23H19BO10 | |
| Molar mass | 466.19 g/mol |
| Appearance | red solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Rubrocurcumin is a red-colored dye that is formed by the reaction of curcumin and borates.
Synthesis
The reaction of curcumin with borates in presence of oxalic acid produces rubrocurcumin.[1]
Characteristics
Rubrocurcumin produces a red colored solution.
Rubrocurcumin is a neutral molecule, while rosocyanine is ionic. In rubrocurcumin, one molecule of curcumin is replaced with oxalate compared to rosocyanine.
Complexes with boron such as rubrocurcumin are called 1,3,2-dioxaborines.[1]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Rohde, D. (2002). Darstellung und Eigenschaftsuntersuchungen an 1,3,2-Dioxaborinen mit variablen Coliganden am Boratom [Presentation and characterization of 1,3,2-dioxaborins with variable coligands on the boron atom] (Dissertation). University Halle.
Further reading
- Spicer, G. S.; Strickland, J. D. H. (1952). "Compounds of Curcumin and Boric Acid. Part II. The Structure of Rubrocurcumin". Journal of the Chemical Society (London) 1952 (art. 907): 4650–4653. doi:10.1039/JR9520004650.
 |

