Brinkmann graph
| Brinkmann graph | |
|---|---|
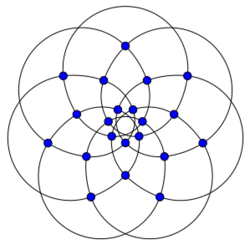 The Brinkmann graph | |
| Named after | Gunnar Brinkmann |
| Vertices | 21 |
| Edges | 42 |
| Radius | 3 |
| Diameter | 3 |
| Girth | 5 |
| Automorphisms | 14 (D7) |
| Chromatic number | 4 |
| Chromatic index | 5 |
| Book thickness | 3 |
| Queue number | 2 |
| Properties | Eulerian Hamiltonian |
| Table of graphs and parameters | |
In the mathematical field of graph theory, the Brinkmann graph is a 4-regular graph with 21 vertices and 42 edges discovered by Gunnar Brinkmann in 1992.[1] It was first published by Brinkmann and Meringer in 1997.[2]
It has chromatic number 4, chromatic index 5, radius 3, diameter 3 and girth 5. It is also a 3-vertex-connected graph and a 3-edge-connected graph. It is the smallest 4-regular graph of girth 5 with chromatic number 4.[2] It has book thickness 3 and queue number 2.[3]
By Brooks’ theorem, every k-regular graph (except for odd cycles and cliques) has chromatic number at most k. It was also known since 1959 that, for every k and l there exist k-chromatic graphs with girth l.[4] In connection with these two results and several examples including the Chvátal graph, Branko Grünbaum conjectured in 1970 that for every k and l there exist k-chromatic k-regular graphs with girth l.[5] The Chvátal graph solves the case k = l = 4 of this conjecture and the Brinkmann graph solves the case k = 4, l = 5. Grünbaum's conjecture was disproved for sufficiently large k by Johannsen, who showed that the chromatic number of a triangle-free graph is O(Δ/log Δ) where Δ is the maximum vertex degree and the O introduces big O notation.[6] However, despite this disproof, it remains of interest to find examples and only very few are known.
The chromatic polynomial of the Brinkmann graph is x21 - 42x20 + 861x19 - 11480x18 + 111881x17 - 848708x16 + 5207711x15 - 26500254x14 + 113675219x13 - 415278052x12 + 1299042255x11 - 3483798283x10 + 7987607279x9 - 15547364853x8 + 25384350310x7 - 34133692383x6 + 36783818141x5 - 30480167403x4 + 18168142566x3 - 6896700738x2 + 1242405972x (sequence A159192 in the OEIS).
Algebraic properties
The Brinkmann graph is not a vertex-transitive graph and its full automorphism group is isomorphic to the dihedral group of order 14, the group of symmetries of a heptagon, including both rotations and reflections.
The characteristic polynomial of the Brinkmann graph is [math]\displaystyle{ (x-4)(x-2)(x+2)(x^3-x^2-2x+1)^2 }[/math][math]\displaystyle{ (x^6+3x^5-8x^4-21x^3+27x^2+38x-41)^2 }[/math].
Gallery
The chromatic number of the Brinkmann graph is 4.
References
- ↑ Brinkmann, G. "Generating Cubic Graphs Faster Than Isomorphism Checking." Preprint 92-047 SFB 343. Bielefeld, Germany: University of Bielefeld, 1992.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Brinkmann, G. and Meringer, M. "The Smallest 4-Regular 4-Chromatic Graphs with Girth 5." Graph Theory Notes of New York 32, 40-41, 1997.
- ↑ Jessica Wolz, Engineering Linear Layouts with SAT. Master Thesis, University of Tübingen, 2018
- ↑ "Graph theory and probability", Canadian Journal of Mathematics 11: 34–38, 1959, doi:10.4153/CJM-1959-003-9.
- ↑ "A problem in graph coloring", American Mathematical Monthly (Mathematical Association of America) 77 (10): 1088–1092, 1970, doi:10.2307/2316101.
- ↑ "ω, Δ, and χ", Journal of Graph Theory 27 (4): 177–212, 1998, doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0118(199804)27:4<177::AID-JGT1>3.0.CO;2-K.
External links
 |




