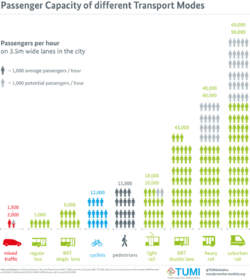
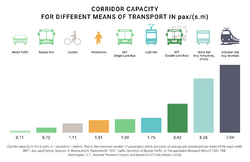
Passengers per hour per direction
Passengers per hour per direction (p/h/d),[1] passengers per hour in peak direction[2] (pphpd) or corridor capacity[3][4] is a measure of the route capacity of a rapid transit or public transport system.
Definition
The corridor capacity in the passenger transport field refers to the maximum number of people which can be safely and comfortably transported per unit of time over a certain way with a defined width. The corridor capacity does not measure the number of vehicles which can be transported over such way, since the nuclear objective of passenger mobility is to transport passengers, not vehicles.[5][6]
In terms of quantities defined within the International System of Units, the corridor capacity may be measured in units of [math]\displaystyle{ \mathrm{s}^{-1}\cdot \mathrm{m}^{-1} }[/math], i.e., the maximum number of passengers per second per meter of the corridor's width. An approximately equivalent concept in physics is volumetric flux.
Directional flow
Many public transport systems handle a high directional flow of passengers— often traveling to work in a city in the morning rush hour and away from the said city in the late afternoon. To increase the passenger throughput, many systems can be reconfigured to change the direction of the optimized flow. A common example is a railway or metro station with more than two parallel escalators, where the majority of the escalators can be set to move in one direction. This gives rise to the measure of the peak-flow rather than a simple average of half of the total capacity.
See also
- Annual average daily traffic – Measurement of how many vehicles travel on a certain road
- Patronage (transportation)
- Crush load
- Headway – Distance between vehicles in a transit system measured in time or space
- Passenger load factor – Capacity utilization of public transport
- Traffic flow – Study of interactions between travellers and infrastructure
- Urban planning
References
- ↑ United Kingdom Parliament, Integrated Transport: The Future of Light Rail and Modern Trams in Britain Inquiry, Memorandum by Transport for London (LR 77) , 2005-08-10.
- ↑ U.S. Department of Transportation, Report on South American Bus Rapid Transit Field Visits: Tracking the Evolution of the TransMilenio Model , 2007-12, retrieved 2008-07-10.
- ↑ "Corridor capacity of different modes of transportation (people/hr on a 3.5 mile-wide lane). Source: Modifi ed from Breithaupt, 2010". https://www.researchgate.net/figure/Corridor-capacity-of-different-modes-of-transportation-people-hr-on-a-35-mile-wide_fig8_262030493.
- ↑ "7.4 Calculating Corridor Capacity". https://brtguide.itdp.org/branch/master/guide/system-speed-and-capacity/calculating-corridor-capacity.
- ↑ Asian Development Bank. "Changing Course in Urban Transport, page 55". http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org.in/files/file/changing-course-urban-transport-illustrated-guide.pdf.
- ↑ BOTMA and PAPENDRECHT, HANS and HEIN. "Traffic Operation of Bicycle Traffic". Transportation Research Record: 1320. http://onlinepubs.trb.org/Onlinepubs/trr/1991/1320/1320-009.pdf.
 |