Scoop (utensil)
In common usage, a scoop is any specialized spoon used to serve food.[1]
In the technical terms used by the food service industry and in the retail and wholesale food utensil industries, there is a clear distinction between three types of scoop: the disher, which is used to measure a portion e.g. cookie dough, to make melon balls, and often to serve ice cream (although manufacturers frequently advise against using dishers for ice cream and other frozen foods);[citation needed] ice cream scoops, and the scoop which is used to measure or to transfer an unspecified amount of a bulk dry foodstuff such as rice, flour, or sugar.
Disher
Dishers are usually hemispherical like an ice cream scoop, while measuring scoops are usually cylindrical, and transfer scoops are usually shovel-shaped. Some dishers have mechanical levers which help expel the disher's contents. Traditionally dishers are sized by the number of scoops per quart but may also be sized by ounces, the diameter of the bowl, or the number of tablespoons they hold.
Ice cream scoop
Some higher-end ice cream scoops have a thermally conductive liquid in the handle to help keep the ice cream from freezing to the scoop's metal.[citation needed]
History
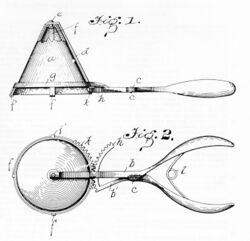
Alfred L. Cralle, a porter in a drug store and at a hotel in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania,[2][3] noticed that servers at the hotel had trouble with ice cream sticking to serving spoons, and he developed an ice cream scoop.[4] On June 10, 1896, Cralle applied for a patent on his invention. He was awarded patent 576,395 on February 2, 1897.[5] The patented "Ice Cream Mold and Disher," was an ice cream scoop with a built-in scraper to allow for one-handed operation.[6][7] Cralle's functional design is reflected in modern ice cream scoops.[8]
Transfer scoop
Transfer scoops (a.k.a. utility scoops) are used to transfer bulk foods from large storage containers to smaller containers, and generally do not have any measurement markings, as their purpose is to transfer, and taking time to adjust the amount in a scoop would slow the transfer rate.
Other types
- Ice scoop
- Coffee scoop
- Spooner
- Dipper
- French fry scoop
- Cheese scoop
Standard sizes
The table below is the standard definition in the U.S. food industry, but actual capacity varies by manufacturer.[9][citation needed]
| Handle Color | Scoop Number (Scoops per Quart) |
Typical Use[10] | U.S. Fluid Ounces (fl. oz.) |
Spoon Equivalent (Tea=tsp. Table=TBS.) |
Metric (mL) |
Diameter (inches) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Orange |
4 | 8.0 | 32.0 16 Tbs.
(1 cup) || 236.6 || 3 5⁄8″
| |||
Teal |
5 | 6.4 | 32.0 12.8 Tbs.
( 0.8 cup) || 189.3 || 3 3⁄8″
| |||
White |
6 | 5.3 | 32.0 10 2⁄3 Tbs.
(2⁄3 cup) ||158|| 3″
| |||
Gray |
8 | ice cream, jumbo cupcakes, mashed potatoes | 4.0 | 24.0 8 TBS.
(1⁄2 cup) ||118|| 2 3⁄4″ | ||
Ivory |
10 | Texas-size muffins, popovers | 3.2 | 19.2 6 2⁄5 Tbs.
(2⁄5 cup) ||95|| 2 5⁄8″ | ||
Green |
12 | Ice cream, Standard muffins | 2.7 | 16.0 5 1⁄3 Tbs.
(1⁄3 cup) ||80|| 2 3⁄8 or 2 1⁄2″ | ||
Sky Blue |
14 | 2.4 | 71 | 2 3⁄8″ | ||
Royal Blue |
16 | Pancakes | 2.0 | 12.0 4 Tbs.
(1⁄4 cup) ||59|| 2 5⁄16″ | ||
Yellow |
20 | ice cream, giant cookies | 1.6 | 09.6 3 1⁄5 Tbs.
(1⁄5 cup) ||47|| 2 1⁄8″ | ||
Red |
24 | regular cupcakes, sorbet, mashed potatoes | 1.3 | 08.0 2 2⁄3 Tbs.
(1⁄6 cup) ||38|| 2″
| ||
Black |
30 | silver-dollar pancakes, candies | 1.1 | 06.4 2 1⁄8 Tbs.
(17⁄128 cup) ||33|| 1 7⁄8″ | ||
Mushroom |
36 | 0.94 | 27.8 | 1 3⁄4″ | ||
Orchid |
40 | mini muffins | 0.8 | 04.8 1 1⁄2 Tbs.
(3⁄32 cup) ||24|| 1 5⁄8″ | ||
Rust |
50 | mini cupcakes, canapés | 0.64 | 32.0 1.28 Tbs.
(0.08 cup) || 19 || | ||
Pink |
60 | large cookies | 0.53 | 03.2 3 1⁄5 tsp.
(1⁄15 cup) ||16||
| ||
Plum |
70 | cookies | 0.46 | 02.7 2 3⁄4 tsp.
(11⁄192 cup) ||14|| 1 1⁄4 | ||
Orange |
100 | chocolate truffles | 0.32 | 01.9 1 8⁄9 tsp.
(17⁄432 cup) ||9||
|
See also
- Ladle
References
- ↑ "Scoop utensil United States Patent 6733056". Freepatentsonline.com. 2002-06-14. http://www.freepatentsonline.com/6733056.html. Retrieved 2014-03-11.
- ↑ "Afro-American Notes". The Pittsburgh Press. February 14, 1897. https://www.newspapers.com/clip/8589074/the_pittsburgh_press/.
- ↑ "The Gifts of African American Innovation". February 12, 2014. http://www.tutufoundationusa.org/tag/alfred-cralle/.
- ↑ "Alfred L. Cralle (1866–1920)" (in en). https://www.blackpast.org/african-american-history/cralle-alfred-l-1866-1920/.
- ↑ "United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) : nombre de brevets délivrés à certains quelques opérateurs de télécommunications". http://pdfpiw.uspto.gov/.piw?Docid=00576395.
- ↑ "History of Ices & Ice Cream". http://whatscookingamerica.net/History/IceCream/IceCreamHistory.htm. Retrieved May 28, 2018.
- ↑ "A. L. Cralle Ice Cream Mold and Disher Patent Number 576395". http://pdfpiw.uspto.gov/.piw?docid=00576395&SectionNum=2&IDKey=58EAA3B731DC&HomeUrl=http://patft.uspto.gov/netahtml/PTO/patimg.htm. Retrieved May 28, 2018.
- ↑ Stradley, Linda (2015-05-14). "Ice Cream History, Whats Cooking America" (in en-US). What's Cooking America. https://whatscookingamerica.net/History/IceCream/IceCreamHistory.htm.
- ↑ Chen, Kit. "Disher (aka ice cream scoop) sizes". http://bowlofplenty.blogspot.com/2009/08/dishers-aka-ice-cream-scoops.html. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
- ↑ "Dishers". Archived from the original on 23 May 2007. https://web.archive.org/web/20070523094518/http://www.kitchenconservatory.com/dishers.htm. Retrieved 30 October 2016.
 |