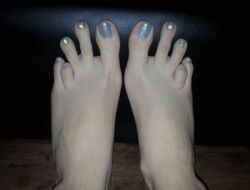
Medicine:Brachymetatarsia
| Brachymetatarsia | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Hypoplastic metatarsal |
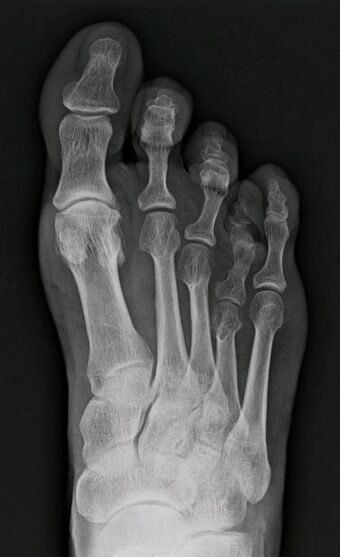 | |
| X-ray of congenital brachymetatarsia involving fourth metatarsal bone | |
| Symptoms | Discomfort with shoe wearing[1] |
Brachymetatarsia is a rare malformation that causes one or more toes to be abnormally short. The condition is characterized by a metatarsal arch shortness of more than 5 mm. The condition is more common in females, and the incidence reported in the literature ranges from 0.02% to 0.05%. Brachymetatarsia appears to be the result of epiphyseal plate retardation or premature closure. The etiology may be congenital and idiopathic, posttraumatic, postinfection, iatrogenic, or secondary to a systemic disease such as cancer, sickle cell disease, pseudohyperparathyroidism, Turner's syndrome, Down's syndrome, Apert syndrome, athyroidism, or osteodystrophy.[2]
It most frequently involves the fourth metatarsal. If it involves the first metatarsal, the condition is known as Morton's syndrome. Treatment is via a number of differing surgical procedures.[3]
Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis
Congenital causes include: Aarskog syndrome, Turner syndrome, Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy, maternal ingestion of thalidomide during pregnancy and Apert syndrome. Can be caused by a trauma, although the exact mechanism is not known.[3]
Treatment
Symptoms may be treated by wearing wider shoes to relieve pressure, or the patient can wear padding around the toes. Surgery is also an option, if the pain and discomfort cannot be treated, or for cosmetic reasons. In this procedure, the short metatarsal is typically cut and a piece of bone is grafted between the two ends. In some cases, an external fixator may be attached to the metatarsal with pins. Within the external fixator is an adjustable screw that must be turned (per doctors' orders) to lengthen the gap between bone segments, so the bone will regrow to the appropriate shape.[3]
Following surgery, crutches or a knee scooter should be used to keep all weight off the surgically repaired foot for 3 months. After this period, orthopedic shoes or boots may be used.[4]
Epidemiology
Brachymetatarsia is found to occur more frequently in women than men.[3] Brachymetatarsia affecting the first metatarsal of the foot is the most common type of brachymetatarsia, with approximately 22% of the population being affected by it.[5]
References
- ↑ "Brachymetatarsia". 2021-06-15. https://www.orthobullets.com/pediatrics/4082/brachymetatarsia.
- ↑ Zhu, David; Lefèvre, Maxime; Fernandez, Andréa; Galois, Laurent (2022-03-10). "Brachymetatarsia: Surgical Management, Case Report, and Literature Review". Case Reports in Orthopedics (Hindawi Limited) 2022: 1–6. doi:10.1155/2022/8253096. ISSN 2090-6757. PMID 35310144.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 "Brachymetatarsia". Foot Ankle Clin 9 (3): 555–70, ix. September 2004. doi:10.1016/j.fcl.2004.05.002. PMID 15324790.
- ↑ "Home". http://www.healthcommunities.com/.
- ↑ "What is Morton's Toe" (in en). 2016-03-24. https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Mortons-Toe.aspx.
Further reading
- Lamm, Bradley M.; Lamm, Tyler B. (2023). "Brachymetatarsia: A Classification for Surgical Treatment". The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery (Elsevier BV) 62 (1): 132–149. doi:10.1053/j.jfas.2022.06.002. ISSN 1067-2516. PMID 35817705.
- Córdoba-Fernández, Antonio; Vera-Gómez, Maria Luisa (2018). "Literature Review on Brachymetatarsia". Orthopaedic Nursing (Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)) 37 (5): 292–302. doi:10.1097/nor.0000000000000487. ISSN 0744-6020. PMID 30247412.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|
 |