Medicine:Senior–Løken syndrome
| Senior–Løken syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Renal dysplasia-retinal aplasia syndrome |
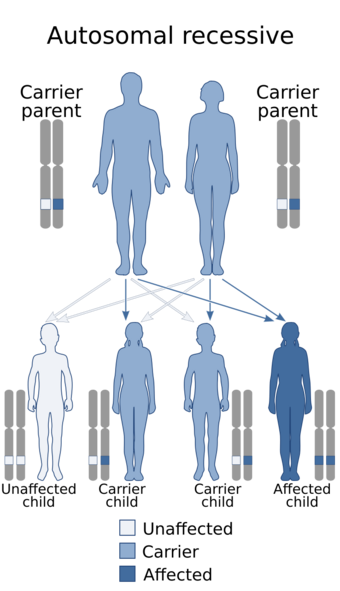 | |
| Senior–Løken syndrome is an autosomal recessive inherited condition | |
Senior–Løken syndrome is a congenital eye disorder, first characterized in 1961.[1][2][3] It is a rare, ciliopathic, autosomal recessive disorder characterized by juvenile nephronophthis and progressive eye disease.[4]
Genetics
Genes involved include:
| Type | OMIM | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| SLSN1 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 266900 | NPHP1 |
| SLSN3 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 606995 | unknown |
| SLSN4 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 606996 | NPHP4 |
| SLSN5 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 609254 | NPHP5/IQCB1[5] |
| SLSN6 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 610189 | NPHP6/CEP290 |
| SLSN7 | Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 613615 | SDCCAG8 |
Pathophysiology
The cause of Senior–Løken syndrome type 5 has been identified to mutation in the NPHP1 gene which adversely affects the protein formation mechanism of the cilia.[6]
Relation to other rare genetic disorders
Recent findings in genetic research have suggested that a large number of genetic disorders, both genetic syndromes and genetic diseases, that were not previously identified in the medical literature as related, may be, in fact, highly related in the genetypical root cause of the widely varying, phenotypically-observed disorders. Such diseases are becoming known as ciliopathies. Known ciliopathies include primary ciliary dyskinesia, Bardet–Biedl syndrome, polycystic kidney and liver disease, nephronophthisis, Alström syndrome, Meckel–Gruber syndrome and some forms of retinal degeneration.[4]
Diagnosis
Treatment
References
- ↑ synd/1861 at Who Named It?
- ↑ "Juvenile familial nephropathy with tapetoretinal degeneration. A new oculorenal dystrophy". Am. J. Ophthalmol. 52: 625–33. 1961. doi:10.1016/0002-9394(61)90147-7. PMID 13910672.
- ↑ "Hereditary renal dysplasia and blindness". Acta Paediatrica 50 (2): 177–84. 1961. doi:10.1111/j.1651-2227.1961.tb08037.x. PMID 13763238.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Badano, Jose L.; Norimasa Mitsuma; Phil L. Beales; Nicholas Katsanis (2006). "The Ciliopathies: An Emerging Class of Human Genetic Disorders". Annual Review of Genomics and Human Genetics 7 (1): 125–148. doi:10.1146/annurev.genom.7.080505.115610. PMID 16722803..
- ↑ "Nephrocystin-5, a ciliary IQ domain protein, is mutated in Senior-Loken syndrome and interacts with RPGR and calmodulin". Nat. Genet. 37 (3): 282–8. March 2005. doi:10.1038/ng1520. PMID 15723066.
- ↑ Davenport, James R.; Bradley K. Yoder (2005). "An incredible decade for the primary cilium : a look at a once-forgotten organelle". American Journal of Physiology. Renal Physiology (American Physiological Society) 289 (6): F1159–F1169. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00118.2005. PMID 16275743..
External links
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 266900 Senior-Løken syndrome; Renal dysplasia retinal aplasia; Juvenile nephronophthisis with Leber amaurosis at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
- Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM) 606996 Senior-Løken syndrome 4 at NIH's Office of Rare Diseases
- NCBI Genetic Testing Registry
| Classification |
|
|---|---|
| External resources |
 |

