Chemistry:Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate)
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
PubChem CID
|
|
| Properties | |
| (C9H3F5O2)n | |
| Molar mass | variable |
| Appearance | white solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
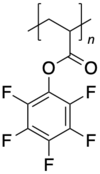
Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) (variously abbreviated PPFPA, PolyPFPA, PPfpA, or PolyPfpA) is a highly fluorinated polymer. It features the pentafluorophenyl ester functionality, from which its properties and applications result. It is most commonly used in post-polymerization modification to synthesize functional polyacrylamides or polyacrylates.[1] As such, it is advantageous to poly(N-acryloyl succinimide) due to its broader solubility in organic solvents as well as its higher stability towards hydrolysis.[citation needed]
Synthesis
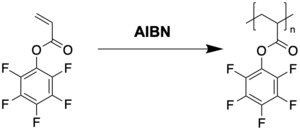
Commonly poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) is synthesized by free radical polymerization of the monomer pentafluorophenyl acrylate.[2]
Additionally, pentafluorophenyl acrylate can be successfully polymerized by RAFT polymerization yield homopolymers, copolymers, or block copolymers.[3]
It has been shown that poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) can also be prepared by pulsed plasma deposition.[4]
Chemical properties
Reactivity
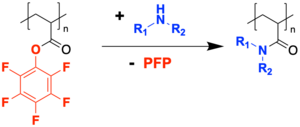
Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) is a polymeric active ester and hence features an inherent reactivity towards nucleophiles such as amines.[5] It is therefore used in the preparation of polyacrylamides by reacting it with amines.
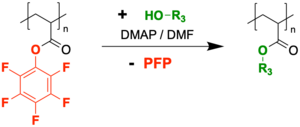
Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) can also be used in a transesterification by reacting it with alcohols when auxiliary DMAP and DMF are used, allowing for the synthesis of polyacrylate homopolymers and copolymers.[5]
Low refractive index polymers
Polymers are known for featuring low refractive indices typically in the range from 1.3 to 1.8, with fluorinated polymers exhibiting refractive indices in the range from 1.3 to 1.4. As such, poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) has been explored as a crosslinkable cladding for optical fibers when copolymerized with glycidyl methacrylate.[6]
Applications
Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) finds application in the synthesis of functional polymers by post-polymerization modification.[7] Applications of the resulting polyacrylamides can be found in drug delivery, functional surfaces, and nanoparticles.
References
- ↑ Xue, Wenwen; Mutlu, Hatice; Theato, Patrick (2020-05-05). "Post-polymerization modification of polymeric active esters towards TEMPO containing polymers: A systematic study" (in en). European Polymer Journal 130: 109660. doi:10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2020.109660. ISSN 0014-3057. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014305720305863.
- ↑ , Wikidata Q112792308
- ↑ , Wikidata Q57352340
- ↑ Noël, Caroline (2009). Plasma polymerisation: study and application (Doctoral thesis). Durham University.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 , Wikidata Q57358055
- ↑ Robertsson, Mats; Anders Hult & Claire Pitois, "Optical guide", EP patent 0932844, published 2006-05-24, assigned to Telefonaktiebolaget LM Ericsson AB
- ↑ Theato, Patrick; Klok, Harm-Anton (2012). Functional Polymers by Post-Polymerization Modification - Concepts, Guidelines, and Applications. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. ISBN 9783527331154.
 |