Biology:FAM222A
 Generic protein structure example |
Family with sequence similarity 222 member A or Aggregatin is a protein of unknown function. In humans it is encoded by the gene FAM222A. Aggregatin's cellular function is not well understood, however it has been implicated in Alzheimer's disease.[1]
Gene
FAM222A is also called C12orf34.[2] It is located on chromosome 12 at q24.11.[3] It encompasses 56,672 bp.[3] The mRNA is 3,685 bp while the coding region is 1,359 bp.[3]
FAM222A is highly expressed in the brain and spinal cord.[4] It is expressed to a lesser extent in the cerebellum, pituitary gland, adrenal gland and testis.[4]
mRNA
It has 3 different splice variants of mRNA.[2] The most common mRNA is 3,685 bp while the coding region is 1,359 bp.[2] The mRNA consists of three exons and has two different isoforms in humans. The Kozak Sequence is not very well conserved in FAM222A and it has a non-canonical polyadenylation site.
Protein
Aggregatin is a protein made of 452 amino acids.[3] It contains a domain of unknown function called pfam15258 which is 200 amino acids long.[3]
It has been found to be part of protein plaques formed in the brains of patients with Alzheimer's disease.[1]
FAM222A has an unusually high amount of prolines with a 6 segment run from amino acids 392 to 397.
Structurally, FAM222A has 5 domains which are connected by linker regions.[5][6]
Analysis of the amino acid sequence suggests that FAM222A is localized in the nucleus.[7]
Expression and regulation
FAM222A is highly expressed in the brain and to a lesser extent in the adrenal glands.[4][8]
Alzheimer’s disease seems to cause an increase in FAM222A in the brain, but other degenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s do not.[9][10]
Interacting proteins
FAM222A has been found to interact with mainly transcription factors. These include mainly pre-B-cell leukemia transcription factors and Homeobox Meis proteins.[11]
Homologs
FAM222A has only one paralog in humans, FAM222B which is also not well characterized.[12] These two proteins only share about 20% identity.
It has many orthologs in other organisms but is restricted to jawed vertebrates, as far back as bony and cartilaginous fish.[13] Overall the protein is well conserved with a lowest identity of around 50% but certain regions are very strictly conserved such as the beginning of pfam15258 as well as the last 60-70 amino acids on the C terminus.[2]
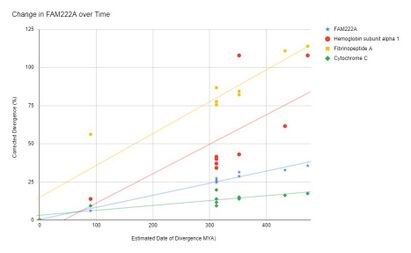
The protein appears to be changing very slowly even in distantly related animals. It is changing at a rate just slightly higher than Cytochrome C, a highly conserved protein.]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "FAM222A encodes a protein which accumulates in plaques in Alzheimer's disease". Nature Communications 11 (1): 411. January 2020. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-13962-0. PMID 31964863.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 "FAM222A Gene - GeneCards | F222A Protein | F222A Antibody". https://www.genecards.org/cgi-bin/carddisp.pl?gene=FAM222A&keywords=Fam222a.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 "FAM222A family with sequence similarity 222 member A [Homo sapiens (human) - Gene - NCBI"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?cmd=Retrieve&dopt=full_report&list_uids=84915.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "GTEx Portal". https://gtexportal.org/home/gene/FAM222A.
- ↑ "PHYRE2 Protein Fold Recognition Server". http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/~phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index.
- ↑ "I-TASSER server for protein structure and function prediction". https://zhanglab.ccmb.med.umich.edu/I-TASSER/.
- ↑ "Using neural networks for prediction of the subcellular location of proteins". Nucleic Acids Research 26 (9): 2230–6. May 1998. doi:10.1093/nar/26.9.2230. PMID 9547285.
- ↑ "Gene Detail :: Allen Brain Atlas: Mouse Brain". https://mouse.brain-map.org/gene/show/130520.
- ↑ "GDS4758 / 7958577". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/tools/profileGraph.cgi?ID=GDS4758:7958577.
- ↑ "GDS3129 / 226487_at". https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/geo/tools/profileGraph.cgi?ID=GDS3129:226487_at.
- ↑ "FAM222A protein (human) - STRING interaction network". https://string-db.org/cgi/network.pl?taskId=qEcilP1DAPxp.
- ↑ "FAM222B family with sequence similarity 222 member B [Homo sapiens (human) - Gene - NCBI"]. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene?Db=gene&Cmd=DetailsSearch&Term=55731.
- ↑ "FAM222A orthologs" (in en). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/84915/ortholog/.
 |