Biology:Chama lazarus
| Chama lazarus | |
|---|---|

| |
| The lower (attachment) valve of a shell of Chama lazarus from the Philippines , on display at the Museo Civico di Storia Naturale di Milano | |
| |
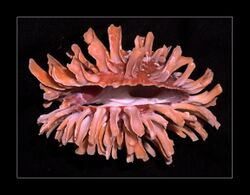
| Chama lazarus from the Philippines showing the leaf-like branching spines | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Mollusca |
| Class: | Bivalvia |
| Order: | Venerida |
| Family: | Chamidae |
| Genus: | Chama |
| Species: | C. lazarus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Chama lazarus Linnaeus, 1758
| |
Chama lazarus, common name the Lazarus jewel box, is a species of cemented saltwater clam, a marine bivalve mollusc in the family Chamidae, the jewel boxes.
Description
Chama lazarus has a shell that usually grows to about 75 mm, with a maximum length of 140 mm. The outer surface of the shell is reddish or pale brown, and shows long, branched, leaf-like spines.
Distribution
This invasive species is widespread in the Indo-West Pacific, from East Africa, including the Red Sea, to Melanesia; north to Japan and south to Queensland. The distribution includes Australia, Philippines, New Caledonia, Papua New Guinea, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, Eswatini, Solomon Islands, Taiwan, South Africa, British Indian Ocean Territory, Fiji, Thailand, Comoros, Madagascar, Micronesia and Guam.
Habitat
It can be found on rocks and corals in low intertidal zone and sublittoral to depths of about 30 m.
References
- OBIS Indo-Pacific Molluscan Database
- Gwannon
- Ftp.fao[yes|permanent dead link|dead link}}]
- WoRMS
- Encyclopedia of life
Wikidata ☰ Q3658509 entry
 |

