Biology:Rufous-tailed scrub robin
| Rufous-tailed scrub robin | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Muscicapidae |
| Genus: | Cercotrichas |
| Species: | C. galactotes
|
| Binomial name | |
| Cercotrichas galactotes (Temminck, 1820)
| |
| |
range map
| |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
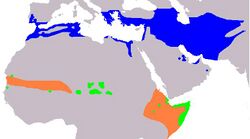
The rufous-tailed scrub robin (Cercotrichas galactotes) is a medium-sized member of the family Muscicapidae. Other common names include the rufous scrub robin, rufous bush chat, rufous bush robin[2] and the rufous warbler.[3] It breeds around the Mediterranean and east to Pakistan . It also breeds south of the Sahara from the Sahel region east to Somalia; these African birds are sometimes considered to be a separate species, the African scrub robin (C. minor). It is partially migratory, wintering in Africa (Kenya, South Sudan, Ethiopia, Somalia) and India . This is a very rare visitor to northern Europe.
The scientific name is from Ancient Greek. Cercotrichas is from kerkos, "tail" and trikhas, "thrush", and galactotes means resembling milk, from gala, "milk".[4]
The rufous-tailed scrub robin is a bird of dry open country with bushes and shrubs. It builds its nest a few feet off the ground; there are three to five eggs in a typical clutch.
The rufous-tailed scrub robin is larger than the European robin. It has brown upper parts, whitish under parts, and a prominent whitish supercilium and a dark eye-stripe. The western race has a paler, warmer brown back than birds in southeastern Europe and Asia. The long rufous tail is frequently fanned, showing the black and white tips of the tail feathers. The adult male and female have similar plumage and the juvenile resembles the adult but is paler. These birds feed on insects mostly caught on the ground. Their clear thrush-like song has a sad tone.
Description
Adult male and female rufous-tailed scrub robin look alike and measure about 6 inches (150 mm) long with relatively long legs and a large rounded tail. The upper parts are a rich brownish chestnut, with the rump and uppertail coverts rather more rufous. There is a distinct curved, creamy-white broad streak from the nostrils to behind the eye and a dark brown line through the eye. The under-eye area is whitish and the ear coverts pale brown. The eye and the beak are both brown but the lower mandible of the beak has a greyish base. The underparts are buffish white, with the chin, central belly and undertail coverts paler than the other parts. The feathers of the wing are dark brown, fringed on the leading edge with buff and on the trailing edge with pale chestnut-brown and with the secondaries tipped with white. The central pair of feathers on the tail are bright rufous-chestnut with narrow black tips and the rest a similar colour with white tips and adjacent broad black bands. The legs and feet are pale brown. Juveniles are similar in appearance but generally a paler sandy-brown colour. The plumage is moulted in the autumn and prior to this, the white tips of the tail feathers may have become reduced in size or worn off.[3]
The song is a somewhat lark-like but often disjointed series of notes, sometimes clear and loud but at other times soft, and is sung from an elevated position near the top of a tree, on a pole or on a wire.[3] It has been described as having a sad tone.[citation needed]
Distribution and habitat
The rufous-tailed scrub robin is a partial migrant. Its breeding range extends from Portugal, southern Spain and the Balkan Peninsula, through the Middle East to Iraq, Kazakhstan and Pakistan. In Africa it breeds from Morocco to Egypt and south of the Sahara as far east as Somalia. It is an uncommon vagrant to northern Europe. It winters in North Africa and eastwards to India. Its habitat is dry scrubby open country with patches of dense bushes in lowlands or foothills; where it is numerous, it may also be found in parks, vineyards and large gardens.[3]
The rufous-tailed scrub robin has an extensive range, estimated at 4.3 million square kilometres (1.66 million square miles), and a large population, including an estimated 96 to 288 thousand individuals in Europe. As the European range is somewhere between a quarter and half of the global range, the global population may range from 196 thousand to 1.15 million individuals. The population size appeared to be stable in 2013 and the bird was not believed to approach the thresholds for the population decline criteria of the IUCN Red List of Threatened Species (i.e., declining more than 30% in ten years or three generations), and was then evaluated as being of "Least Concern".[5]
Behaviour
The rufous-tailed scrub robin is found flitting among dense cover but also in more open positions on trees, the tops of bushes and on posts. It is frequently seen on the ground hopping about and flaring and bobbing its tail up and down. When perched it also displays its tail in this way and also sometimes droops its wings before giving them a little flick forward. It feeds mainly on the ground on insects such as beetles, grasshoppers and the larvae of butterflies and moths, and on earthworms, turning over the leaf litter to find its prey.[3]
The male rufous-tailed scrub robin has an unusual display flight involving a downward swoop with uplifted wings and may sing while displaying. The nest is built a few feet off the ground in a bush, a hedge of prickly pear, on a tree stump or other concealed place. It is usually well-hidden and is untidily built of grasses, stems, roots and other fibres. The inside is neatly cup-shaped and is lined with fine roots, hairs and often a piece of snakeskin.[3] A clutch of four to five (occasionally fewer) eggs is laid. The eggs average about 22 by 16 millimetres (0.87 in × 0.63 in) and have a pale greenish or greyish-white background colour liberally sprinkled with greyish-brown spots.[3]
Ecology
Sometimes the rufous-tailed scrub robin is found in association with a woodchat shrike (Lanius senator), perhaps nesting in a neighbouring tree. The woodchat shrike perches near the top of a tree, ever alert to sparrowhawks, buzzards and other aerial predators while the scrub robin perches on a bush or lower branch, scanning the ground for the approach of snakes, cats, weasels, foxes, genets, ocellated lizards and other predators. Both birds are adept at luring away predators by flying towards them to attract their attention and then flitting away from the nest site through the undergrowth. The rufous-tailed scrub robin can recognise the warning cries of other species of bird and take appropriate action.[6]
Gallery
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2019). "Cercotrichas galactotes". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T22709936A155484275. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2019-3.RLTS.T22709936A155484275.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22709936/155484275. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lepage, Dennis. "Rufous-tailed Scrub-Robin (Cercotrichas galactotes) (Temminck, 1820)". Avibase. http://avibase.bsc-eoc.org/species.jsp?lang=EN&avibaseid=E4672C85DEAD098A.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 Witherby, H. F., ed (1943). Handbook of British Birds, Volume 2: Warblers to Owls. H. F. and G. Witherby Ltd.. pp. 101–103.
- ↑ Jobling, James A. (2010). The Helm Dictionary of Scientific Bird Names. London, United Kingdom: Christopher Helm. pp. 97, 169. ISBN 978-1-4081-2501-4. https://archive.org/details/Helm_Dictionary_of_Scientific_Bird_Names_by_James_A._Jobling.
- ↑ "Rufous-tailed Scrub-robin Erythropygia galactotes". Birdlife International. http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/speciesfactsheet.php?id=6633.
- ↑ Daly, Stephen (2011-07-13). "Rufous Bush Robin (Cercotrichas galactotes)". http://andalucianguides.blogspot.co.uk/2013/07/rufous-bush-robin-cercotrichas.html.
Wikidata ☰ Q607027 entry
 |








