Biology:Brown-hooded gull
| Brown-hooded gull | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Laridae |
| Genus: | Chroicocephalus |
| Species: | C. maculipennis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Chroicocephalus maculipennis (Lichtenstein, MHC, 1823)
| |
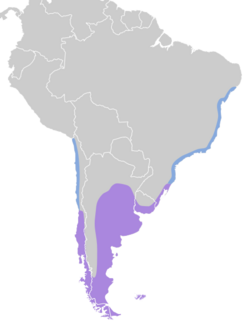
| |
Nonbreeding Year-round
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Larus maculipennis | |
The brown-hooded gull (Chroicocephalus maculipennis) is a species of gull found in Argentina, Brazil, Chile, the Falkland Islands, and Uruguay. Its specific epithet, maculipennis, means 'spotted wings' (macula + penna). It is a white bird with a brown head and red beak and feet.
Description
The mature bird has a dark brown head and throat with a white semicircle around the posterior part of the eye, while the neck, chest and abdomen are white. The beak and legs are red. The primary flight feathers are dark gray, while the secondaries and covert feathers are a lighter gray. This bird may be confused with the Franklin's gull. There is no significant sexual dimorphism.[1]
Distribution and habitat
This species is found in South America, breeding from Argentine and Chilean Patagonia, the Falkland Islands and Uruguay. In winter, its range extends up to the coasts of north Chile and central Brazil.[2] Its natural habitats include freshwater lakes, intertidal marshes, river banks, and open fields.[1]
Ecology and behavior
These are gregarious birds. Their diet consists primarily of insects, carrion, and food items obtained through kleptoparasitism from other birds. In particular they steal crabs from the red-gartered coot (Fulica armillata) and clams from the American oystercatcher (Haematopus palliatus). The profitability of stealing from these birds is 3.5 times higher for the coots than the oystercatchers.[3] They build floating nests among aquatic vegetation at the edges of ponds and lakes. Three to four eggs are usually laid.[1]
The black-headed duck has a brood parasite relationship with the brown-hooded gull in which a female will lay an egg in the nest of a brown-hooded gull with the intent of having the host gull incubate the egg instead of herself.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Garay Nancul, G; Guineo Nancul, O (1997). Torres Del Paine - Fauna Flora and Mountains (1st ed.). Punta Arenas, Chile: Paraguaya 126. p. 74.
- ↑ "Species factsheet: Larus maculipennis". BirdLife International. Cambridge, England. 2013. http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/speciesfactsheet.php?id=3239. Retrieved 2013-02-13.
- ↑ García, Germán Oscar; Favero, Marco; Vassallo, Aldo Iván (2012). "Interspecific kleptoparasitism by Brown-headed Gulls (Chroicocephalus maculipennis) on two hosts with different foraging strategies: a comparative approach". Emu 112 (3): 227–233. doi:10.1071/MU11085.
- ↑ MaurícioI,Giovanni N.; Bencke, Glayson Ariel; Repenning, Márcio; Machado, Diogenes Borges; Dias, Rafael A.; Bugoni, Leandro (2013). "Review of the breeding status of birds in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil". Iheringia. Série Zoologia 103 (2): 163. doi:10.1590/S0073-47212013000200012.
- Pons J.M., Hassanin, A., and Crochet P.A.(2005). Phylogenetic relationships within the Laridae (Charadriiformes: Aves) inferred from mitochondrial markers. Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution 37(3):686-699
Wikidata ☰ Q1268078 entry
 |





