Biology:Pied heron
| Pied heron | |
|---|---|

| |
| At Fogg Dam Conservation Reserve | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Pelecaniformes |
| Family: | Ardeidae |
| Genus: | Egretta |
| Species: | E. picata
|
| Binomial name | |
| Egretta picata (Gould, 1845)[2]
| |
| |
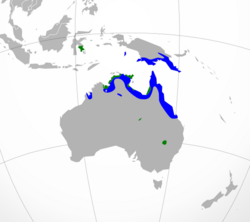
| Distribution. Green: year-round breeding, blue: nonbreeding. | |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The pied heron (Egretta picata), also known as the pied egret[4] is a bird found in coastal and subcoastal areas of monsoonal northern Australia as well as some parts of Wallacea and New Guinea.
Taxonomy
The species was originally described by ornithologist John Gould in 1845. Recent taxonomists put this species in the genus Egretta. There are no recognised subspecies.[5]
Description
It is a small heron, 43–55 cm long, with dark slaty wings, body, and crested head, with a white throat and neck. The appearance is similar to the white-necked heron.[4] Males (247–280 g) are heavier than females (225–242 g), but the two are similar in appearance.[6]
Immature birds lack the crest as well as the dark colouring on the head and may look like small versions of the white-necked heron. The juveniles were once classified as a separate species.[6]
Distribution and habitat
Its habitat mainly comprises a range of wetlands and wet grasslands.
Behaviour
Call
The call of the pied heron is a loud 'awk' or 'ohrk' in flight.[4] Soft cooing is given around the nest.[6] Little else is known about vocalisations.[6]
Breeding
Breeding takes place from February to May.[4] It nests in trees above the water, including mangroves, often colonially with other species of heron. 1–2 blue-green eggs are laid in a shallow platform of sticks.[4]
Feeding
It feeds on insects, frogs, crabs, fish and other small aquatic animals. Insects are the most important source of food.[6] It may feed alone or in groups of up to a thousand individuals.[6]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2019). "Egretta picata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2019: e.T22697037A155512365. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-3.RLTS.T22697037A155512365.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22697037/155512365. Retrieved 12 November 2021.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2008). "Ardea picata". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2008. https://www.iucnredlist.org/details/144680/0. Retrieved 9 February 2009. Database entry includes justification for why the species is listed as least concern.
- ↑ BirdLife International (2006) Species factsheet: Ardea picata. Downloaded from http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/species/index.html?action=SpcHTMDetails.asp&sid=3727 on 25/02/2010
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.3 4.4 Pizzey, Graham; Knight, Frank (1997). Field Guide to the Birds of Australia. Sydney, Australia: HarperCollinsPublishers. p. 111. ISBN 0-207-18013-X.
- ↑ "Pied Heron, Egretta picata, Taxonomy". http://www.damisela.com/zoo/ave/otros/ciconi/ardei/day/picata/taxae.htm.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 Kushlan, James Anthony; Hancock, James; Thelwell, David (2005). The Herons. Oxford University Press. p. 170. ISBN 0-19-854981-4.
Bibliography
- Marchant, S.; & Higgins, P.J. (Coordinators). (2000). Handbook of Australian, New Zealand and Antarctic Birds. Vol.1: Ratites to Ducks. Oxford University Press: Melbourne. ISBN:978-0-19-553068-1
Wikidata ☰ Q420729 entry
 |





