Biology:Olive-green tanager
| Olive-green tanager | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Passeriformes |
| Family: | Mitrospingidae |
| Genus: | Orthogonys Strickland, 1844 |
| Species: | O. chloricterus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Orthogonys chloricterus (Vieillot, 1819)
| |
| |
The olive-green tanager (Orthogonys chloricterus) is a species of bird in the family Mitrospingidæ. It is endemic to Brazil .[1]
Taxonomy and systematics
The olive-green tanager and the three other species in family Mitrospingidæ were previously placed in family Thraupidæ, the "true" tanagers. A 2013 publication detailed how they did not belong there and proposed the new family for them.[2] The North and South American Classification Committees of the American Ornithological Society accepted the new placement in July 2017 and March 2019, respectively.[3][4] The International Ornithological Committee (IOC) followed suit in January 2018.[1]
The olive-green tanager is the only member of its genus and has no subspecies.[1]
Description
The olive-green tanager is 18 to 19 cm (7.1 to 7.5 in) long. The adult is olive green above and dull yellow below; it has a tinge of olive on the sides and flanks.[5]
Distribution and habitat
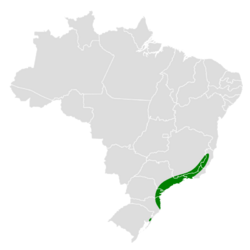
The olive-green tanager is found only in southeastern Brazil, from Espírito Santo state south to eastern Santa Catarina and northeastern Rio Grande do Sul. It inhabits the interior and edges of humid montane forest at elevations of 900 to 1,800 m (3,000 to 5,900 ft).[5]
Behavior
Feeding
The olive-green tanager's diet is primarily insects, though it also eats fruit. It typically forages in flocks of its own species that may number up to 20 individuals but more usually have about eight. It feeds in the mid- to upper levels of the forest, usually picking prey from leaves, and it also sallies for flying insects.[5]
Breeding
One olive-green tanager was noted carrying nest material to a bromeliad in a large tree. No other information has been published about its breeding phenology.[5]
Vocalization
The olive-green tanager's song has been rendered as "tséé-si, si, si, tséé-si, si, si."[6] Its call is a buzzy "tseee" [7] and it also calls "wheek!" while foraging.[5][8]
Status
The IUCN has assessed the olive-green tanager as being of Least Concern.[9] "Despite local population declines and fragmentation, its long-term viability should be assured if protection continues for the parks and reserves where it remains."[5]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Gill, F.; Donsker, D.; Rasmussen, P., eds (2022-02-01). "IOC World Bird List (v 12.1)". https://www.worldbirdnames.org/bow/warblers/.
- ↑ Barker, F. Keith; Burns, Kevin J.; Klicka, John; Lanyon, Scott M.; Lovette, Irby J. (2012-12-29). "Going to extremes: contrasting rates of diversification in a recent radiation of New World passerine birds" (in en-US). Systematic Biology 62 (2): 298–320. doi:10.1093/sysbio/sys094. PMID 23229025. https://academic.oup.com/sysbio/article/62/2/298/1671243. Retrieved 2022-05-30.
- ↑ Chesser, R. Terry; Burns, Kevin J.; Cicero, Carla; Dunn, Jon L.; Kratter, Andrew W.; Lovette, Irby J.; Rasmussen, Pamela C.; Remsen, J. V. Jr. et al. (2017-07-05). "Fifty-eighth supplement to the American Ornithological Society's Check-list of North American Birds" (in en-US). The Auk 134 (3): 751–773. doi:10.1642/AUK-17-72.1.
- ↑ Remsen, J. V. Jr.; Areta, Juan Ignacio; Bonaccorso, Elisa; Claramunt, Santiago; Jaramillo, Alvaro; Lane, Daniel F.; Pacheco, José Fernando; Robbins, Mark B. et al. (2022-01-31). "A classification of the bird species of South America" (in en-US). American Ornithological Society. https://www.museum.lsu.edu/~Remsen/SACCBaseline.htm.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 5.2 5.3 5.4 5.5 Hilty, Steven; Juana, Eduardo de (2020-03-04). Hoyo, J. del; Elliott, A.; Sargatal, J. et al.. eds (in en-US). Olive-green Tanager (Orthogonys chloricterus), version 1.0.. Ithaca, New York: Cornell Lab of Ornithology. doi:10.2173/bow.olgtan1.01. https://birdsoftheworld.org/bow/species/olgtan1/1.0/introduction. Retrieved 2022-05-30.
- ↑ Gagliardi, Ricardo. "XC471138 · Olive-green Tanager · Orthogonys chloricterus" (in en-US). https://www.xeno-canto.org/471138.
- ↑ Fischer, Jerome. "XC340702 · Olive-green Tanager · Orthogonys chloricterus" (in en-US). https://www.xeno-canto.org/340702.
- ↑ Boesman, Peter. "XC227019 · Olive-green Tanager · Orthogonys chloricterus" (in en-US). https://www.xeno-canto.org/227019.
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedIUCN
Wikidata ☰ Q278819 entry
 |


