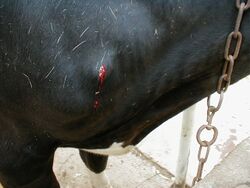
Biology:Verminous haemorrhagic dermatitis (cattle)
Verminous haemorrhagic dermatitis is a filariasis of cattle marked by a cutaneous haemorrhagic nodule. It is referred sometimes to as "summer wound" (German Sommerwunden).
It is caused by infestation with the nematode Parafilaria bovicola. Transmission involves fly vectors of the genus Musca, which ingest microfilariae when feeding on the skin lesions. [1]
The disease has been reported in Bulgaria, France , Germany , Morocco, Sweden, Tunisia, and especially South Africa .
In Germany, the nodules are known to develop on the upper side on the body. In Morocco, the haemorrhagic lesions are mainly seen on the belly, neck and forelimbs, where it can lead to a wide plages of subcutaneous necrosis, with swelling of the arm.
Ivermectin is efficient for individual treatments of the illness. But surgical excision, although very haemorrhagic, is far more efficient.
A similar disease, sometimes referred to as Cascado, occurs in Asia (Indonesia, Malaysia) and is caused by Stephanofilaria species.
Epidemiology
Epidemiology differs among the countries in which it has been reported, and is dependent upon temperature and rainfall patterns, and the subsequent multiplication of the fly vectors.
In Germany, the verminous nodules start in May and June, 2 to 4 weeks after the beginning of pasture feeding. They heal spontaneously in October and November. [2]
In Morocco, the disease is observed in years when heavy rainfalls occur in March and April. Numerous cases are then observed in April and May, in the immediate surroundings of the ponds. Some cases will heal spontaneously, but some others lead to wide subcutaneous lesions which require a veterinary treatment. The repartition and gravity of the skin lesions suggests that the causative agent may be slightly different from the one observed in Western Europe. [3]
External links
References
- ↑ Johannes Kaufmann, Parasitic infections of domestic animals, Birkhäuser Verlag, Basel, ISBN:3-7643-5115-2, p. 106-107.
- ↑ Gustav Rosenberger, Krankheiten des Rindes, Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin, ISBN:3-489-61716-9. p. 912-913
- ↑ Lucien Mahin, Observations on diseases of cattle in Morocco, 1977-2008, unpublished data.
 |