Biology:Karlodinium veneficum
| Karlodinium veneficum | |
|---|---|
| |
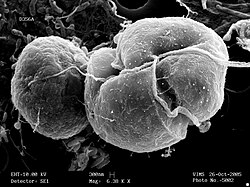
| Scanning electron microscope image of Karlodinium veneficum (right) feeding on Rhodomonas | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Clade: | Diaphoretickes |
| Clade: | SAR |
| Clade: | Alveolata |
| Phylum: | Myzozoa |
| Superclass: | Dinoflagellata |
| Class: | Dinophyceae |
| Order: | Gymnodiniales |
| Family: | Kareniaceae |
| Genus: | Karlodinium |
| Species: | K. veneficum
|
| Binomial name | |
| Karlodinium veneficum (D.Ballantine) J.Larsen 2000
| |
Karlodinium veneficum is a species of dinoflagellates belonging to the family Kareniaceae.[1] This species is predominantly inhabiting aquatic environments, particularly in temperate coastal regions.
Karlodinium veneficum genome sizes have been reported as ~20 pg/cell[2] and 4 pg/cell.[3]
This phytoplankton has the capacity to produce harmfull toxins, specifically karlotoxins, which have been associated with detrimental phenomena such as harmful algae blooms.[4] These blooms have been documented globally, spanning regions from South Africa[5] and Europe[6] to Australia, North America, and China. The repercussions of K. veneficum blooms include not only ecological concerns, also substantial economic and environmental impacts.
The species-specific toxins produced by K. veneficum, known as karlotoxins, belong to the amphidinol-like compound class, exhibiting hemolytic, ichthyotoxic, and cytotoxic properties. The toxins generated by this dinoflagellate have been implicated in massive fish kills during bloom events.[7]
K. veneficum is not confined to solitary blooms but frequently coexists with other phytoplankton species, such as Prorocentrum donghaiense and Karenia mikimotoi.[8] K. veneficum often proliferates into dense blooms following the decline of P. donghaiense.[9]
References
- ↑ "Karlodinium veneficum (D.Ballantine) J.Larsen 2000 :: Algaebase". https://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=44336.
- ↑ Figueroa, Rosa Isabel; Garcés, E.; Bravo, I. (2010). "The use of flow cytometry for species identification and life-cycle studies in dinoflagellates". Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography (Elsevier BV) 57 (3–4): 301–307. doi:10.1016/j.dsr2.2009.09.008. ISSN 0967-0645. Bibcode: 2010DSRII..57..301F.
- ↑ Liu, Yuyang; Hu, Zhangxi; Deng, Yunyan; Shang, Lixia; Gobler, Christopher J.; Tang, Ying Zhong (2021). "Dependence of genome size and copy number of rRNA gene on cell volume in dinoflagellates". Harmful Algae (Elsevier BV) 109: 102108. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2021.102108. ISSN 1568-9883. PMID 34815026.
- ↑ Deeds, Jonathan R; Terlizzi, Daniel E; Adolf, Jason E; Stoecker, Diane K; Place, Allen R (2002-06-01). "Toxic activity from cultures of Karlodinium micrum (=Gyrodinium galatheanum) (Dinophyceae)—a dinoflagellate associated with fish mortalities in an estuarine aquaculture facility". Harmful Algae 1 (2): 169–189. doi:10.1016/S1568-9883(02)00027-6. ISSN 1568-9883. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568988302000276.
- ↑ "Gymnodinium galatheanum Braarud :: AlgaeBase". https://www.algaebase.org/search/species/detail/?species_id=52347.
- ↑ Carreto, J. I. (2001-10-01). "Pigment profile of the ichthyotoxic dinoflagellate Gymnodinium sp. from a massive bloom in southern Chile". Journal of Plankton Research 23 (10): 1171–1175. doi:10.1093/plankt/23.10.1171. ISSN 1464-3774. https://doi.org/10.1093/plankt/23.10.1171.
- ↑ Van Wagoner, Ryan M.; Deeds, Jonathan R.; Satake, Masayuki; Ribeiro, Anthony A.; Place, Allen R.; Wright, Jeffrey L.C. (November 2008). "Isolation and characterization of karlotoxin 1, a new amphipathic toxin from Karlodinium veneficum" (in en). Tetrahedron Letters 49 (45): 6457–6461. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2008.08.103. PMID 20798789. PMC 2928153. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0040403908016250.
- ↑ Zhou, Chengxu; Place, Allen R.; Yan, Xiaojun; Xu, Jilin; Luo, Qijun; William, Ernest; Jiang, Ying (November 2015). "Interactions between Karlodinium veneficum and Prorocentrum donghaiense from the East China Sea" (in en). Harmful Algae 49: 50–57. doi:10.1016/j.hal.2015.08.004. PMID 31093028. PMC 6512812. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1568988315001286.
- ↑ Wang, Rui; Wu, Jiajun; Zhou, Shiwen; Cao, Ruobing; Chan, Leo Lai (2020-09-01). "A preliminary study on the allelopathy and toxicity of the dinoflagellate Karlodinium veneficum". Marine Pollution Bulletin 158: 111400. doi:10.1016/j.marpolbul.2020.111400. ISSN 0025-326X. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025326X2030518X.
Wikidata ☰ Q68462642 entry
 |

