Biology:Yellow-footed gull
| Yellow-footed gull | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Laridae |
| Genus: | Larus |
| Species: | L. livens
|
| Binomial name | |
| Larus livens Dwight, 1919
| |
| |
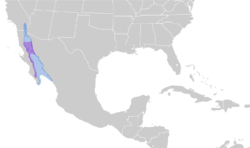
| Distribution Non-Breeding Year-round
| |
The yellow-footed gull (Larus livens) is a large gull, closely related to the western gull and thought to be a subspecies until the 1960s. It is endemic to the Gulf of California.
Description
Adults are similar in appearance to the western gull with a white head, dark, slate-colored back and wings, and a thick yellow bill. Its legs are yellow, though first winter birds do display pink legs like those of the western gull. It attains full plumage at three years of age.
This species is tied with slaty-backed gull for the world's fourth-largest gull species and is one of the largest gulls in the world, being slightly larger than the western gull. It measures 53 to 72 cm (21 to 28 in) in length and spans 140 to 160 cm (55 to 63 in) across the wings.[2] The body mass of this species can vary from 930 to 1,500 g (2.05 to 3.31 lb).[2][3] Among standard measurements, the wing chord is 40 to 46 cm (16 to 18 in), the bill is 5.0 to 6.2 cm (2.0 to 2.4 in) and the tarsus is 5.9 to 7.5 cm (2.3 to 3.0 in).[2]
Distribution and habitat
Yellow-footed gulls are native to the Gulf of California in Mexico. Most are non-migratory, but an increasing number have been traveling to California 's Salton Sea and southwards to Sonora during nonbreeding periods. Their breeding habitat is the Gulf of California, where they nest, in April, either independently or in colonies. They are found on sandy and rocky coasts or islands, often with little vegetation.[4]
Behavior
The birds are scavengers as well as foragers, feeding on small fish and invertebrates, carcases of marine mammals and offal, and preying upon seabird chicks and eggs (including pelican eggs).[4] They sometimes scavenge around waste dumps and docks for refuse but seldom fly far inland.[5]
Yellow-footed gulls nest on the beach, a few metres above the upper limits of the highest tides. A pair of birds defends a small territory between the nest and the sea. The nest is a scrape in the sand with a meagre lining of seaweed or dry plant material. Usually, three eggs are laid, olive or buff in color with dark blotches, and incubation is probably done by both parents. The young are fully fledged and leave the nest when they are about seven weeks old.[5]
Status
The population is estimated at about 60,000 individuals and appears to be stable, so the IUCN has rated the species as being of "least concern".[4]
References
- ↑ BirdLife International (2020). "Larus livens". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T22694340A168885266. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T22694340A168885266.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/22694340/168885266. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Gulls: Of North America, Europe, and Asia by Klaus Malling Olsen & Hans Larsson. Princeton University Press (2004). ISBN:978-0691119977.
- ↑ CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses by John B. Dunning Jr. (Editor). CRC Press (1992), ISBN:978-0-8493-4258-5.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 "Species factsheet: Larus livens". BirdLife International. http://www.birdlife.org/datazone/speciesfactsheet.php?id=3224.
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 "Yellow-footed Gull (Larus livens)". Planet of Birds. 2011-07-08. http://www.planetofbirds.com/charadriiformes-laridae-yellow-footed-gull-larus-livens.
- "National Geographic" Field Guide to the Birds of North America ISBN:0-7922-6877-6
- Seabirds, an Identification Guide by Peter Harrison, (1983) ISBN:0-7470-1410-8
- Handbook of the Birds of the World Vol 3, Josep del Hoyo editor, ISBN:84-87334-10-5
- "National Audubon Society" The Sibley Guide to Birds, by David Allen Sibley, ISBN:0-679-45122-6
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q629447 entry
 |


