Biology:Ocypode
| Ocypode | |
|---|---|

| |
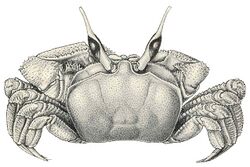
| Horned ghost crab (Ocypode ceratophthalma) from Kona, Hawaii | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Malacostraca |
| Order: | Decapoda |
| Suborder: | Pleocyemata |
| Infraorder: | Brachyura |
| Family: | Ocypodidae |
| Subfamily: | Ocypodinae |
| Genus: | Ocypode Weber, 1795 [1] |
| Type species | |
| Cancer ceratophthalmus Pallas, 1772
| |
| Species | |
|
See text | |
| Synonyms[2] | |
| |
Ocypode is a genus of ghost crabs found in the sandy shores of tropical and subtropical regions throughout the world. They have a box-like body, thick and elongated eyestalks, and one claw is larger than the other in both males and females. They inhabit deep burrows in the intertidal zone. They are primarily nocturnal, and are generalist scavengers and predators of small animals. The genus contains 21 species.
Taxonomy
The genus Ocypode was first established by the German entomologist Friedrich Weber in 1795, using the type species Cancer ceratophthalmus described by the German naturalist Peter Simon Pallas in 1772.[3][2]
Ocypode was previously the only genus classified under the ghost crab subfamily Ocypodinae until 2013, when Katsushi Sakai and Michael Türkay reclassified the gulf ghost crab into a separate genus, Hoplocypode. It belongs to the family Ocypodidae. Ghost crabs of the genus Hoplocypode can be distinguished from those in Ocypode by examining their gonopods. In the former, the first gonopod has a complex hoof-shaped tip, while in the latter they are simple and curved.[2]
Description
Ocypode ghost crabs have deep box-like bodies. The regions on the carapace are usually not clearly defined. They have thick and elongated eyestalks with the cornea occupying most of the lower portion. The eyestalks are also tipped with horn-like projections (styles) in seven species (Ocypode brevicornis, O. ceratophthalma, O. gaudichaudii, O. macrocera, O. mortoni, O. rotundata, and O. saratan). Though these may be shorter or even absent altogether in juvenile specimens. While in O. cursor the eyestalks are tipped with a tuft of bristles (setae). The eyestalks are held vertically when the crab is active.[2][4] Most species have pale-colored bodies that blend in well with the sand,[5] though they are capable of gradually changing body coloration to match their environment and the time of day.[6][7]
The claw-bearing legs (chelipeds) of both sexes are unequal in size, with one much larger than the other. The palm of the claws also possess stridulating (sound-producing) ridges which they use for communication. These ridges are also important morphological characters useful for identifying species. The chelipeds are shorter than the walking legs. The last pair of walking legs (pereiopods) is also usually shorter and thinner than the other pairs of walking legs. A cavity, with edges fringed by long setae are also found in between the bases of the second and third walking legs.[2][4]
Ecology
Ocypode ghost crabs construct simple to complex deep burrows in soft sandy and/or muddy substrates. They can be found in sandy beaches, rubble flats, and in estuarine areas. They are nocturnal and are generalist scavengers and predators of small animals.[4][8]
Distribution
Ocypode ghost crabs are found in tropical and subtropical regions throughout the world.[9] Three species are found in the Atlantic Ocean and the Mediterranean Sea and one in the eastern Pacific coast of the Americas. The rest of the species are found in the western Pacific and the Indian Ocean to the tip of southern Africa.[2]
Species
Ocypode currently contains 21 valid species. The ghost crab formerly known as O. occidentalis was transferred to its own genus Hoplocypode in 2013. O. longicornuta, O. platytarsis, O. pygoides and O. sinensis were determined to be synonyms of O. ceratophthalma, O. brevicornis, O. convexa and O. cordimanus respectively.[2]
| Species | Common names | Description | Image |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ocypode africana De Man, 1881 |
Medium-sized species found in the eastern Atlantic coast of Africa from Mauritania to Namibia. It is sympatric with O. cursor but can easily be distinguished from the latter by the absence of the tuft of bristles on the tip of their eyes.[2] | ||
| Ocypode brevicornis H. Milne-Edwards, 1837 |
Large-sized species found in Oman, India , Sri Lanka, and the Nicobar Islands. They can be distinguished from other species of Ocypode in the Indian Ocean by the naked propodi of their first and second pair of walking legs and by the 23 to 28 tubercles on their stridulating ridge. Their eyestalks possess styles.[2] |  Ocypode brevicornis from Chennai, India | |
| Ocypode ceratophthalma (Pallas, 1772) |
horned ghost crab or horn-eyed ghost crab[10][11] | Medium to large-sized species. They are one of the most widespread species in Ocypode, being found in the entirety of the Indian Ocean (except the Red Sea); and eastwards toward Polynesia and Clipperton Island, though they are not known from the eastern Pacific coast of the Americas. Their eyestalks possess styles, and they are frequently confused with similar species which share their distribution range (especially juveniles). They can be distinguished by a stridulating ridge of 10 to 11 interspaced tubercles on the upper third, 8 thick striae on the central third, and 20 to 30 closely spaced tubercles on the lower third; as well as by their slender gonopod with a palp, and the pointed tip of their smaller claw.[2] | |
| Ocypode convexa Quoy & Gaimard, 1824 |
golden ghost crab,[12][13] western ghost crab,[14] or yellow ghost crab[15] | Large-sized species found in Western Australia, from Broome to Perth. They can be distinguished by the forward-facing triangular outer edges of their eye orbits, pointed smaller claws, a stridulating ridge of 19 to 24 tubercles, and a fringe of bristles on the upper margin of the propodi of the first and second walking legs.[2] |  Ocypode convexa from Gnaraloo, Australia |
| Ocypode cordimanus Latreille, 1818 |
smooth-handed ghost crab[16] | Medium-sized species. They are one of the most widespread species in Ocypode, being found in the western Indian Ocean (including the Red Sea) to the French Polynesia in the western Pacific. As their common name implies, they can be distinguished by the absence of stridulating ridges on the palm of their claws.[2] |  Ocypode cordimanus from New South Wales, Australia |
| Ocypode cursor (Linnaeus, 1758) |
tufted ghost crab[17] | Large-sized species found in the eastern Atlantic, from Mauritania to Namibia; as well as the Mediterranean Sea, from Egypt to southern Greece. They are easily distinguished by the characteristic tuft of bristles on the end of their eyestalks.[2] | |
| Ocypode fabricii H. Milne-Edwards, 1837 |
Medium-sized species found in Northern and Western Australia, from Darwin to Shark Bay. They closely resemble O. jousseaumei, but they are not found from the same localities.[2] | ||
| Ocypode gaudichaudii H. Mile-Edwards & Lucas, 1843 |
painted ghost crab[18] | Medium to large-sized species found in the eastern Pacific coast of the Americas, from Guatemala to Chile . They share their distribution range with Hoplocypode occidentalis but are easily distinguishable by their bright coloration and the presence of styles on their eyestalks.[2] | |
| Ocypode jousseaumei (Nobili, 1905) |
Small to medium-sized species found only in the Gulf of Aden and the Gulf of Oman. They are very similar to O. fabricii, but they are not found in the same localities.[2] | ||
| Ocypode kuhlii De Haan, 1835 |
Kuhl's ghost crab | Medium to large-sized species found in the Nicobar Islands, southern Thailand, Indonesia, and Papua New Guinea. They can be distinguished by a stridulating ridge of about 10 interspaced tubercles. The propodi of their first to fourth pair of walking legs do not possess bristles on the upper and lower surfaces.[2] | |
| Ocypode macrocera H. Milne-Edwards, 1852 |
Medium-sized species found in Pakistan , India (including the Nicobar Islands), Sri Lanka, and Myanmar. In adult males, the outer edges of the eye orbits are tooth-shaped and project forward. The palm of the claws are densely covered with tubercles on the upper surface, with distinctively serrated upper and lower margins. The stridulating ridge has 35 to 56 tubercles with striae. The tip of the smaller claw is characteristically blunt. Their eyestalks possess styles.[2] | ||
| Ocypode madagascariensis Crosnier, 1965 |
Medium-sized species found in Madagascar and the southeastern coast of Africa (from Mozambique to Natal, South Africa). Its carapace is covered densely with rough tubercles on the upper surface and wider than it is long. The outer edges of the eye orbits are broadly triangular and project forward. Their stridulating ridge has 20 to 30 tubercles.[2] |  Ocypode madagascariensis from Madagascar | |
| Ocypode mortoni George, 1982 |
Small-sized species found in South China and southern Japan. It is closely related to O. stimpsoni which is also found in the same regions, but can be distinguished by the presence of styles on their eyestalks. They also share the same range with O. ceratophthalmus (which also possess styles), but O. mortoni have 35 to 71 striae on their stridulating ridges and their smaller claws have broadly rounded to flattened tips.[2] | ||
| Ocypode nobilii De Man, 1902 |
Small-sized species found in the Gulf of Thailand, and the Malaysian Peninsula to northern Borneo. They are very similar to O. stimpsoni but they do not share the same distribution range.[2] | ||
| Ocypode pallidula Jacquinot, 1846 |
pallid ghost crab[3] | Small to medium-sized species. They are one of the most widespread species in Ocypode, being found from Hawaii to the Great Barrier Reef to Madagascar and Mauritius. It has been proposed that this species may actually be composed of two cryptic species, but it remains unclear without further molecular genetic tests. Their stridulating ridges are composed of 30 to 42 thick striae in males and 17 to 29 in females. The smaller claw is pointed.[2] |  Ocypode pallidula from Point Lookout, Queensland, Australia |
| Ocypode pauliani Crosnier, 1965 |
Medium-sized species endemic to Madagascar. They possess 7 to 13 tubercles on their stridulating ridges. The smaller claw is pointed.[2] | ||
| Ocypode quadrata (Fabricius, 1787) |
Atlantic ghost crab[3] | Medium to large-sized species found in the western Atlantic, from Massachusetts in the United States to Rio Grande do Sul in Brazil . They are easily distinguished as they are the only species of Ocypode in the western Atlantic.[2] | |
| Ocypode rotundata Miers, 1882 |
Large-sized species found in the southern coast of the Arabian Peninsula to northern India (from Oman to Bombay), including the Persian Gulf. They are very similar to O. saratan but can be distinguished by having 10 to 15 irregularly spaced elongated tubercles with striae on their stridulating ridges and a thumb-like palp on their gonopods. Their eyestalks possess styles.[2] | ||
| Ocypode ryderi Kingsley, 1880 |
pink ghost crab[19][20] | Medium-sized species found in the east coast of Africa, from Abd al Kuri of southern Somalia to Port Elizabeth of South Africa , and also the Seychelles. They can easily be distinguished by the presence of a characteristic red band along the inner edges of their legs.[2] | |
| Ocypode saratan (Forskål, 1775) |
Medium to large-sized species found in the Red Sea. Very common species in the Red Sea, and one of only two species known from there (O. cordimanus has also been recorded in the Red Sea, but only rarely). Also known from Madagascar through Indian Ocean to the Western Pacific. Their eyestalks possess styles.[2] | ||
| Ocypode stimpsoni Ortmann, 1897 |
Small-sized species found in China , the Korean Peninsula, and Japan . They closely resemble O. mortoni but can easily be distinguished because they lack styles on their eyestalks.[2] |  Ocypode stimpsoni from Nagasaki, Japan |
See also
- Heloecius - the semaphore crab
References
- ↑ Sammy De Grave et al. (2009). "A classification of living and fossil genera of decapod crustaceans" (PDF). Raffles Bulletin of Zoology Suppl. 21: 1–109. https://lkcnhm.nus.edu.sg/app/uploads/2017/06/s21rbz1-109.pdf.
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 2.18 2.19 2.20 2.21 2.22 2.23 2.24 2.25 2.26 2.27 Katsushi Sakai; Michael Türkay (2013). "Revision of the genus Ocypode with the description of a new genus, Hoplocypode (Crustacea: Decapoda: Brachyura)". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum – Nature 56 (2): 665–793. http://www.qm.qld.gov.au/~/media/Documents/QM/About%20Us/Publications/Memoirs%20-%20Nature/N56-2/qmn56-2-sakaiturkay.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 DecaNet (2023). "Ocypode Weber, 1795". WoRMS. World Register of Marine Species. http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=106970.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Mary J. Rathbun (1918). "The Grapsoid crabs of America". Bulletin of the United States National Museum 97: 1–461. doi:10.5479/si.03629236.97.i. https://archive.org/details/grapsoidcrabsofa00rath.
- ↑ Gary C. B. Poore; Shane T. Ahyong (2004). Marine Decapod Crustacea of Southern Australia: A Guide to Identification. CSIRO Publishing. p. 496. ISBN 9780643069060. https://archive.org/details/marinedecapodcru00poor.
- ↑ Jonathan P. Green (1964). "Morphological color change in the Hawaiian ghost crab Ocypode ceratophthalma (Pallas)". The Biological Bulletin 126 (3): 407–413. doi:10.2307/1539309. http://www.biolbull.org/content/126/3/407.full.pdf.
- ↑ Martin Stevens; Cheo Pei Rong; Peter A. Todd (2013). "Colour change and camouflage in the horned ghost crab Ocypode ceratophthalmus". Biological Journal of the Linnean Society 109: 257–270. doi:10.1111/bij.12039.
- ↑ Pat Garber (2006). "Phantoms in the Surf: Ghost Crabs". Ocracoke Wild: A Naturalist's Year on an Outer Banks Island. Parkway Publishers. pp. 94–98. ISBN 978-1-933251-31-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=KF9lKLEgkt0C&pg=PA97.
- ↑ George Karleskint, Richard Keith Turner & James Small (2009). "Intertidal communities". Introduction to Marine Biology (3rd ed.). Cengage Learning. pp. 356–411. ISBN 978-0-495-56197-2. https://books.google.com/books?id=0JkKOFIj5pgC&pg=PA377.
- ↑ "Ghost crabs". Marine Invertebrates of the National Park of American Samoa. University of Hawaii. November 10, 2009. http://www.botany.hawaii.edu/basch/uhnpscesu/htms/NPSAinvr/fish_pops/ocypod/crab01.htm.
- ↑ "Horn-eyed ghost crab Ocypode ceratophthalma". Wild Singapore. May 2009. http://www.wildsingapore.com/wildfacts/crustacea/crab/ocypodoidea/ceratophthalmus.htm.
- ↑ Western Australian Museum (2011). "Creature Feature - Haunted Beaches: The fleet-footed Ghost Crabs". Government of Western Australia. http://museum.wa.gov.au/explore/blogs/museummarine/creature-feature-haunted-beaches-fleet-footed-ghost-crabs.
- ↑ Naturaliste Marine Discovery Centre. "Golden Ghost Crab". Government of Western Australia. Archived from the original on November 12, 2013. https://archive.today/20131112105805/http://www.nmdc.com.au/fishy-fun-learning/marine-life-in-focus/golden-ghost-crab/.
- ↑ SpeciesBank (February 7, 2007). "Ocypode convexa (Family Ocypodidae)". Department of the Environment, Australian Government. http://www.environment.gov.au/cgi-bin/species-bank/sbank-treatment.pl?id=78342.
- ↑ Cherie Louise Leeden (2003). Quaternary coastal evolution adjacent to southern Ningaloo Reef, Western Australia: Implications for land use planning (PDF) (Thesis). Curtin University of Technology.
- ↑ Sharon Edgley (2011). "Ocypode cordimana". Great Barrier Reef Invertebrates. University of Queensland. http://www.gbri.org.au/Species/Ocypodecordimanus.aspx.
- ↑ "Ocypode cursor". SeaLifeBase. UBC - Canada. http://www.sealifebase.fisheries.ubc.ca/summary/Ocypode-cursor.html.
- ↑ Thomas J. Trott (1988). "Note on the foraging activities of the painted ghost crab Ocypode gaudichaudii H. Milne Edwards & Lucas in Costa Rica (Decapoda, Brachyura)". Crustaceana 55 (2): 217–219. doi:10.1163/156854088x00546.
- ↑ Lynne Matthews (2007). The Coastal Guide of South Africa. Johannesburg, South Africa: Jacana Media. p. 72. ISBN 978-1-77009-248-8.
- ↑ G. M. Branch; M. L. Branch; C. L. Griffiths; L. E. Buckley (2007). Two Oceans: a Guide to the Marine Life of Southern Africa. Struik Publishers. p. 96. ISBN 1-77007-633-6. https://archive.org/details/twooceansguideto00bran.
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q13908705 entry
 |