Biology:Blandfordia
| Christmas bells | |
|---|---|

| |
| Illustration of Blandfordia grandiflora by Edward Minchen[3] | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Monocots |
| Order: | Asparagales |
| Family: | Blandfordiaceae R.Dahlgren & Clifford[2] |
| Genus: | Blandfordia Sm.[1] |
| |
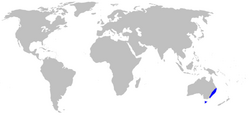
| Distribution | |
Blandfordia, commonly known as Christmas bells,[4] is a genus of four species of flowering plants native to eastern Australia . Christmas bells are tufted, perennial herbs with narrow, linear leaves and up to twenty large, drooping, cylindrical or bell-shaped flowers.
Description
Plants in the genus Blandfordia are tufted, perennial herbaceous monocots with fleshy, fibrous or tuber-like roots from a corm. The leaves are narrow linear, usually crowded in two ranks from the base of the flowering stem. Up to twenty flowers are arranged near the top of the flowering stem that has small, leaf-like bracts. The flowers are usually red with yellow lobes. The sepals and petals are fused to form a tube-shaped, cylindrical or bell-shaped flower with six lobes about one-fifth the length of the tube. There are six stamens fused to the inside wall of the flower tube and the style is linear. Flowering occurs in spring or summer and is followed by the fruit which is a capsule, tapered at both ends and containing a large number of hairy brown seeds.[5]
Taxonomy and naming
The genus Blandfordia was first formally described in 1804 by James Edward Smith from dried specimens sent from Sydney by the colonial surgeon, John White. Smith published the description in Exotic Botany. The name Blandfordia honours George Spencer-Churchill, 5th Duke of Marlborough, the Marquis of Blandford. The type species is Blandfordia nobilis as it was the first described by Smith.[1][6][7][8]
Blandfordia placed in the family Blandfordiaceae of the order Asparagales of the monocots.[2] It is the sole genus in the family Blandfordiaceae. Such a family has only recently been recognized by taxonomists. The APG IV system of 2016 (unchanged from the 1998, 2003 and 2009 versions) recognizes this family.[2][9] Previously various families were suggested.[10]
Four species of are accepted by the Australian Plant Census:[11]
- Blandfordia cunninghamii Lindl. (New South Wales)
- Blandfordia grandiflora R.Br. (Queensland, New South Wales)
- Blandfordia nobilis Sm. (New South Wales)
- Blandfordia punicea (Labill.) Sweet (Tasmania)
Distribution and habitat
Two of the four species of Blandfordia are restricted to New South Wales, a third also occurs in Queensland, and the fourth only occurs in Tasmania. Christmas bells usually grow in heathlands, especially waterlogged sites and mostly in coastal or near-coastal areas although some populations occur on the tablelands.[10]
Use in horticulture
The large, distinctive flowers and long vase life of Blandfordia suggest good commercial potential for the cut flower trade and a small group of producers cater to the domestic and export markets. It is a protected species and in the past over-collecting has caused localised extinction and damage to the habitat of the species.[4]
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 "Blandfordia". https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/apc-format/display/56038. Retrieved 4 June 2023.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (October 2009). "An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG III". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 161 (2): 105–121. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8339.2009.00996.x.
- ↑ Maiden, Joseph (1895–1898). The flowering plants and ferns of New South Wales (Part 5). Government Printer, Sydney. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=chi.14543598;view=1up;seq=104. Retrieved 20 January 2019.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Gollnow, Bettina; Dick, Gordon; Dalley, Paul. "Growing Blandfordia (Christmas bells) commercially". New South Wales Department of Agriculture. http://www.dpi.nsw.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/134837/blandfordia.pdf.
- ↑ Quirico, Anna-Louise. "Blandfordia". Royal Botanic Garden Sydney. http://plantnet.rbgsyd.nsw.gov.au/cgi-bin/NSWfl.pl?page=nswfl&showsyn=&dist=&constat=&lvl=gn&name=Blandfordia.
- ↑ "Blandfordia". APNI. https://id.biodiversity.org.au/instance/apni/458438.
- ↑ Cavanagh, Tony. "Blandfordia in history". Australian Native Plants Society (Australia). http://anpsa.org.au/APOL12/dec98-6.html.
- ↑ Smith, James Edward (1804). Exotic Botany (Volume 1). London: R. Taylor & Co.. pp. 5–6. https://babel.hathitrust.org/cgi/pt?id=hvd.32044106459126;view=1up;seq=33. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- ↑ Angiosperm Phylogeny Group (May 2016). "An update of the Angiosperm Phylogeny Group classification for the orders and families of flowering plants: APG IV". Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 181 (1): 1–20. doi:10.1111/boj.12385.
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 Klaus Kubitzki, Herbert Huber (Prof. rer. nat.) (1998). Flowering plants, Monocotyledons: Lilianae (except Orchidaceae). Springer. p. 150. ISBN 978-3-540-64060-8. https://books.google.com/books?id=FyPVYzL76sMC&q=Blandfordia+nobilis+classification&pg=PA150.
- ↑ "Blandfordia". Australian Plant Census. https://biodiversity.org.au/nsl/services/search/taxonomy?product=APC&tree.id=51209179&name=Blandfordia&inc._scientific=&inc.scientific=on&inc._cultivar=&max=100&display=apc&search=true.
External links
- "Blandfordia Sm.". Atlas of Living Australia. https://bie.ala.org.au/species/https://id.biodiversity.org.au/node/apni/2909807.
Wikidata ☰ Q137543 entry
 |

