Biology:Anthrax (fly)
From HandWiki
Short description: Genus of flies
| Anthrax | |
|---|---|

| |
| Anthrax anthrax | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Arthropoda |
| Class: | Insecta |
| Order: | Diptera |
| Family: | Bombyliidae |
| Tribe: | Anthracini |
| Genus: | Anthrax Scopoli, 1763 |
| Type species | |
| Musca anthrax | |
| Synonyms | |
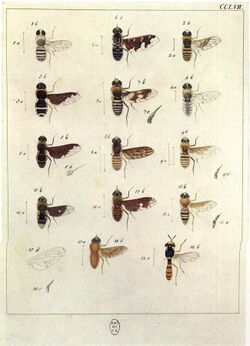
Anthrax is a genus of bombyliid flies, commonly known as "bee-flies" due to their resemblance to bees. Most are dull black flies, and are usually small to medium in size, 4–20 millimetres (0.2–0.8 in), and many species have striking wing patterns.[5]
Anthrax is a very large genus. While worldwide in distribution, most species are from the Palaearctic and Afrotropic regions. The genus includes species parasitic on tiger beetles – an unusual trait among the bee-flies. A. anthrax larvae parasitize bees. Many North American species parasitize solitary wasps.[6][7]
The type species is Musca morio Linnaeus, 1758, later found to be a misidentification of Musca anthrax Schrank, 1781.[8]
Species

Anthrax flies often hover around people and land on them.[6] This one, a member of A. oedipus or a similar species, landed repeatedly on the photographer's jeans.
- Anthrax actuosus Paramonov, 1935[9]
- Anthrax alagoezicus Paramonov, 1935[9]
- Anthrax albofasciatus Macquart, 1840[10]
- Anthrax alruqibi El-Hawagry, 2013[11]
- Anthrax analis Say, 1823[12]
- Anthrax anthrax (Schrank, 1781)[1]
- Anthrax argentatus (Cole, 1919)
- Anthrax artemesia Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax atriplex Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax aureosquamosus Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax bezzianus Paramonov, 1935[9]
- Anthrax binotatus Wiedemann in Meigen 1820[15]
- Anthrax bowdeni Báez, 1983
- Anthrax cascadensis Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax cathetodaithmos Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax chaparralus Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax chionostigma Tsacas, 1962
- Anthrax cintalapa Cole, 1957
- Anthrax columbiensis Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax cybele (Coquillett, 1894)
- Anthrax dentata Becker, 1907
- Anthrax distigma Wiedemann, 1828
- Anthrax francoisi Evenhuis & Greathead, 1999[7]
- Anthrax gideon Fabricius, 1805
- Anthrax giselae François, 1966
- Anthrax greatheadi El-Hawagry, 1998
- Anthrax innublipennis Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax johanni Zaitzev, 1997
- Anthrax koebelei Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax larrea Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax laticellus Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax melanopogon (Becker, 1892)
- Anthrax moursyi El-Hawagry, 1998
- Anthrax nidicola Cole, 1952
- Anthrax nigriventris Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax nitidus Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax oedipus Fabricius, 1805
- Anthrax painteri Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax pauper (Loew, 1869)[16]
- Anthrax pelopeius François, 1966
- Anthrax picea Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax pilosulus Strobl, 1902
- Anthrax plesius (Curran, 1927)
- Anthrax pluricellus Williston, 1901
- Anthrax pluto Wiedemann, 1828[17]
- Anthrax punctulatus Macquart, 1835
- Anthrax seriepunctatus (Osten Sacken, 1886)[18]
- Anthrax slossonae (Johnson, 1913)
- Anthrax snowi Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax stellans (Loew, 1869)[16]
- Anthrax sticticus Klug, 1832
- Anthrax striatipennis Marston, 1970[14]
- Anthrax trifasciatus Meigen, 1804
- Anthrax vallicola Marston, 1963[13]
- Anthrax varius Fabricius, 1794
- Anthrax virgo Egger, 1859
- Anthrax zohrayensis El-Hawagry, 2002
- Anthrax zonabriphagus (Portchinsky, 1895
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Schrank, F. von Paula (1781). Envmeratio insectorvm Avstriae indigenorum. Augustae Vindelicorum [=Augsburg]: Eberhardi Klett et Franck. pp. xxiv + 548 + [4] pp., 4 pls. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/51804#page/7/mode/1up. Retrieved 27 April 2021.
- ↑ Macquart, P.J.M. (1847). Diptères exotiques nouveaux ou peu connus. 2.e supplement. Paris: Roret. pp. 104 pp, 6 pls..
- ↑ Scudder, S. H. (1882). "Nomenclator zoologicus. Part 1. Supplemental list of genera in zoology.". Bulletin of the United States National Museum 19 (1): xxi + 367. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/32440#page/7/mode/1up. Retrieved 15 June 2017.
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Sack, P. (1909). "Die palaearktischen Spongostylinen". Abhandlungen der Senckenbergischen Naturforschenden Gesellschaft 30: 501–548. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/37182881#page/521/mode/1up. Retrieved 14 July 2022.
- ↑ F. M. Hull (1973). Bee flies of the world. The genera of the family Bombyliidae. Washington: Smithsonian Institution Press. pp. 1–687. ISBN 0-87474-131-9. https://archive.org/details/beefliesofworl2861973hull/page/1.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Eaton, Eric R.; Kaufman, Kenn (2007). Kaufman Field Guide to Insects of North America. Houghton Mifflin. p. 292. ISBN 978-0-618-15310-7.
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Evenhuis, N.L.; Greathead, D.J (1999). World catalog of the bee flies (Diptera: Bombyliidae). Leiden: Backhuys Publishers. pp. xlviii + 756 pp. ISBN 90-5782-039-0. OCLC 248444103. http://hbs.bishopmuseum.org/bombcat/. Retrieved 10 July 2022.
- ↑ Magdi S. El-Hawagry; Aly A. El-Moursy; Francis Gilbert; Samy Zalat (2000). "The tribe Anthracini Latreille (Bombyliidae, Diptera) from Egypt". Egyptian Journal of Biology 2: 97–117. http://ecology.nottingham.ac.uk/~plzfg/pdf%20files/2000%20El-Hawagry%20et%20al_Anthracini%20of%20Egypt.pdf.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Paramonov, S.J. (1935). "Beiträge zur Monographie der Gattung Anthrax (Bombyliidae) [I].". Zbirnik Prats Zoologichnogo Muzeyu Ukrain'ska Akademya Nauk 16: 3–31.
- ↑ Macquart, P.J.M. (1840). Diptères exotiques nouveauxou peu connus. Tome deuxieme.--1er partie.. Paris: Roret. pp. 135 pp., 21 pls..
- ↑ El-Hawagry; Khalil; Sharaf; Fadl; Aldawood (2013). "A preliminary study on the insect fauna of Al-Baha Province, Saudi Arabia, with descriptions of two new species". ZooKeys (274): 1–88. doi:10.3897/zookeys.274.4529. PMID 23794807.
- ↑ Say, Thomas (1823). "Descriptions of dipterous insects of the United States". Journal of the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia 3: 73–104. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/24668664#page/83/mode/1up. Retrieved 1 May 2020.
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 13.6 13.7 Marston, N.L. (1963). "A revision of the Nearctic species of the albofasciatus group of the genus Anthrax Scopoli (Diptera: Bombyliidae).". Technical Bulletin, Kansas Agricultural Experimental Station 127: 1–79. https://krex.k-state.edu/dspace/bitstream/handle/2097/25594/LD2668T41962M37.pdf?sequence=1. Retrieved 15 July 2022.
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 14.7 14.8 14.9 Marston, N.L. (1970). "Revision of the New World species of Anthrax (Diptera: Bombyliidae) other than Anthrax albofasciatus group". Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology 43: 1–148. https://repository.si.edu/bitstream/handle/10088/5287/SCtZ-0043-Hi_res.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y. Retrieved 15 July 2022.
- ↑ Meigen, J.W. (1820). Systematische Beschreibung der bekannten europäische n zweiflugeligen Insekten. Aachen: Zweiter Theil. Forstmann. pp. xxxvi + 363. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/item/45915#page/9/mode/1up. Retrieved 8 July 2022.
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Loew, H. (1869). "Diptera Americae septentrionalis indigena. Centuria octava". Berliner Entomologische Zeitschrift 13: 1–52. https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/8343745#page/19/mode/1up. Retrieved 15 July 2022.
- ↑ Wiedemann, Christian Rudolph Wilhelm (1828). Aussereuropäische zweiflügelige Insekten. Als Fortsetzung des Meigenschen Werks. Hamm: Zweiter Theil. Schulz. pp. xxxii + 608 pp., 7 pls.
- ↑ Osten Sacken, C.R. (1886). "Diptera [part]. Biologia Centrali-Americana.". Zoologia-Insecta-Diptera 1: 105–128.
Wikidata ☰ Q401663 entry
 |