Chemistry:Pantoic acid
From HandWiki
Revision as of 22:11, 14 November 2021 by imported>MainAI6 (fixing)
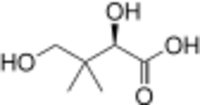
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(2R)-2,4-Dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid | |
| Other names
D-Pantoic acid; D-Pantoate; B(R)-2,4-dihydroxy-3,3-dimethylbutanoic acid
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H12O4 | |
| Molar mass | 148.158 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Tracking categories (test):
Pantoic acid is the alpha hydroxy acid with the formula HOCH2C(CH3)2CH(OH)CO2H. The compound is almost always encountered in a biological context, as an aqueous solution of its conjugate base pantoate HOCH2C(CH3)2CH(OH)CO2-. The amide of pantoic acid with β-alanine is pantothenic acid (vitamin B5),[1] a component of coenzyme A.
Biosynthesis
Its biosynthesis proceeds from ketoisovalerate by hydroxymethylation:
- (CH3)2CHC(O)CO2− + CH2O → HOCH2(CH3)2CC(O)CO2−
This conversion is catalyzed by ketopantoate hydroxymethyltransferase, which gives ketopantoate. Ketopantoate is reduced by ketopantoate reductase to pantoate, using NADH as the hydride source.[2]
The amide derived from pantoic acid and GABA is the pharmaceutical drug hopantenic acid.
References
- ↑ Pantoic acid, Merriam Webster Medical Dictionary
- ↑ Begley, Tadhg P.; Kinsland, Cynthia; Strauss, Erick (2001). "The Biosynthesis of Coenzyme a in Bacteria". Cofactor Biosynthesis. Vitamins & Hormones. 61. pp. 157–171. doi:10.1016/S0083-6729(01)61005-7. ISBN 9780127098616.
External links
 |

