Biology:Barkudia insularis
| Chilka spotted skink | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Reptilia |
| Order: | Squamata |
| Family: | Scincidae |
| Genus: | Barkudia |
| Species: | B. insularis
|
| Binomial name | |
| Barkudia insularis Annandale, 1917
| |
| |
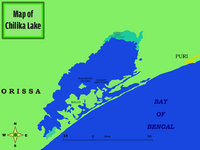
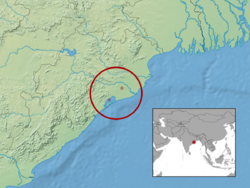
Barkudia insularis, commonly known as the Madras spotted skink, is a critically endangered limbless skink which was described in 1917 by Nelson Annandale and rediscovered in the wild in 2003. Little is known about the species but it was previously believed to be found only in the mangrove habitats near Barkuda Island in Chilka Lake, Odisha, India .[2] Later observations in adjoining parts of Odisha indicate a larger range within the state.[3] The lizard looks like a large earthworm and lives in the subsoil and probably feeds on small arthropods.
The holotype was found in loose earth near the roots of a banyan tree of Badakuda Island of Chilka lake in 1917. Only four reports of the species have been made since its description, all within Odisha: observations in 1917 and 2003 at Barkuda Island in Chilka Lake, a 1979 observation in Nandankanan Zoological Park, and a 2022 observation made near the vicinity of Buguda. The 2022 observation marked the first photograph taken of a live individual of the species.[3]
Taxonomic description
Barkudia (Annandale, Rec. Ind. Mus. xiii, 1917 p. 20 - type species insularis) is characterised by the palatine bones not meeting on the mid-line of the palate, which is toothless; nostril between the nasal and the rostral in an emargination of the latter; supranasals present; pre-frontals and frontoparietals absent; body elongated; no limbs;
Barkudia insularis has the snout depressed, obtusely pointed, projecting strongly beyond the labial margin; rostral large, emarginate laterally to receive the nasal shield; supranasals large, in contact with one another and with the first labial; fronto-nasal broader than long, larger than the frontal; interparietal much larger than the frontal; parietals narrow, obliquely placed, in contact with one another behind it; 3 supraoculars, the first entering the supraciliary margin, the first two in contact with the frontal; 1 large supraciliary in the angle formed by the 3 suboculars; nasal shield comparatively large, the nostril at its anterior extremity; 1 large loreal; a preocular; lower eyelid composed of 2 or 3 opaque scales; upper eyelid vestigial; 4 supralabials, the third below the eye; ear-opening minute; a singly azygous postmental; body elongate with 140 ventral scales between the post-mental and pre-anal plates; 20 smooth scales round the mid body. Tip of the tail blunt and not much narrower than the base of the tail.
Light brown above, each dorsal scale with a central dot; altogether there form 12 or 14 longitudinal lines down the back and along the tail; lower parts whitish; top of head clouded with brown. The type was dug from loose earth at the root of a banyan tree. A second was seen in the same locality by Frederic Henry Gravely in the rainy season of 1919. It burrowed rapidly into the ground.[4]
References
- ↑ Bauer, A.; Srinivasulu, C.; Srinivasulu, B.; Roy, A.D.; Murthy, B.H.C.K.; Molur, S.; Pal, S.; Mohapatra, P. et al. (2020). "Barkudia insularis". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species 2020: e.T2593A176084098. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2020-3.RLTS.T2593A176084098.en. https://www.iucnredlist.org/species/2593/176084098. Retrieved 20 November 2021.
- ↑ Behera, P.K. Ecotech Education and Ecosystem Conservation of the Lake Chilika, Orissa. http://www.ces.iisc.ernet.in/energy/lake2006/programme/programme/proceedings/fullpaper_pdfs/Prashanth.pdf.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Singha, Minati (March 15, 2022). "Rare, endangered legless lizard spotted for 4th time since 1917 in Odisha" (in en). https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/bhubaneswar/rare-endangered-legless-lizard-spotted-for-4th-time-since-1917-in-odisha/articleshow/90233675.cms.
- ↑ Smith, M. A. 1941 Fauna of British India. Reptilia and Batrachia. p. 352-353
Notes
- Annandale, N. 1917 A new Genus of Limbless skinks from an Island in the Chilka Lake Rec.Ind. Mus. 13: 20
- Biswas, S. or Acharjyo, L.N. (1979) A Note on the Distribution of Barkudia insularis, a Rare Limbless Lizard from Orissa J. Bombay Nat. Hist. Soc. 76: 524-525
- Das, Indraneil; Dattagupta, Basudeb 1997 Rediscovery of the holotypes of Ophisops jerdoni Blyth, 1853 and Barkudia insularis Annandale, 1917. Hamadryad 22 (1): 53-55
External links
Wikidata ☰ Q309309 entry
 |